Virtual reality is advancing rapidly, opening up new possibilities for user interaction in digital environments. Designing user interfaces and experiences in VR requires a fresh approach, different from traditional screen-based platforms. Unique challenges include creating intuitive spatial interactions, managing motion controls, and ensuring user comfort to prevent motion sickness. Understanding these challenges is essential for developing effective and engaging VR applications.
In this blog post, we will examine user-centric principles for UI/UX design in almost any virtual reality app development company. Topics will include best practices for spatial design, guidelines for intuitive controls, and strategies to enhance user comfort. We will also discuss common mistakes to avoid and offer practical tips that can be applied immediately. By focusing on the user's needs and expectations, designers can create immersive VR experiences that are both enjoyable and accessible.
Whether you are a seasoned designer exploring virtual reality or new to the field, this guide aims to provide clear and actionable insights. Our focus is on delivering information without unnecessary technical jargon, making it easier for you to apply these principles in your work. The goal is to help you understand the unique aspects of VR design and how to implement user-centric strategies effectively.
The Significance of UI/UX Design for VR Experiences
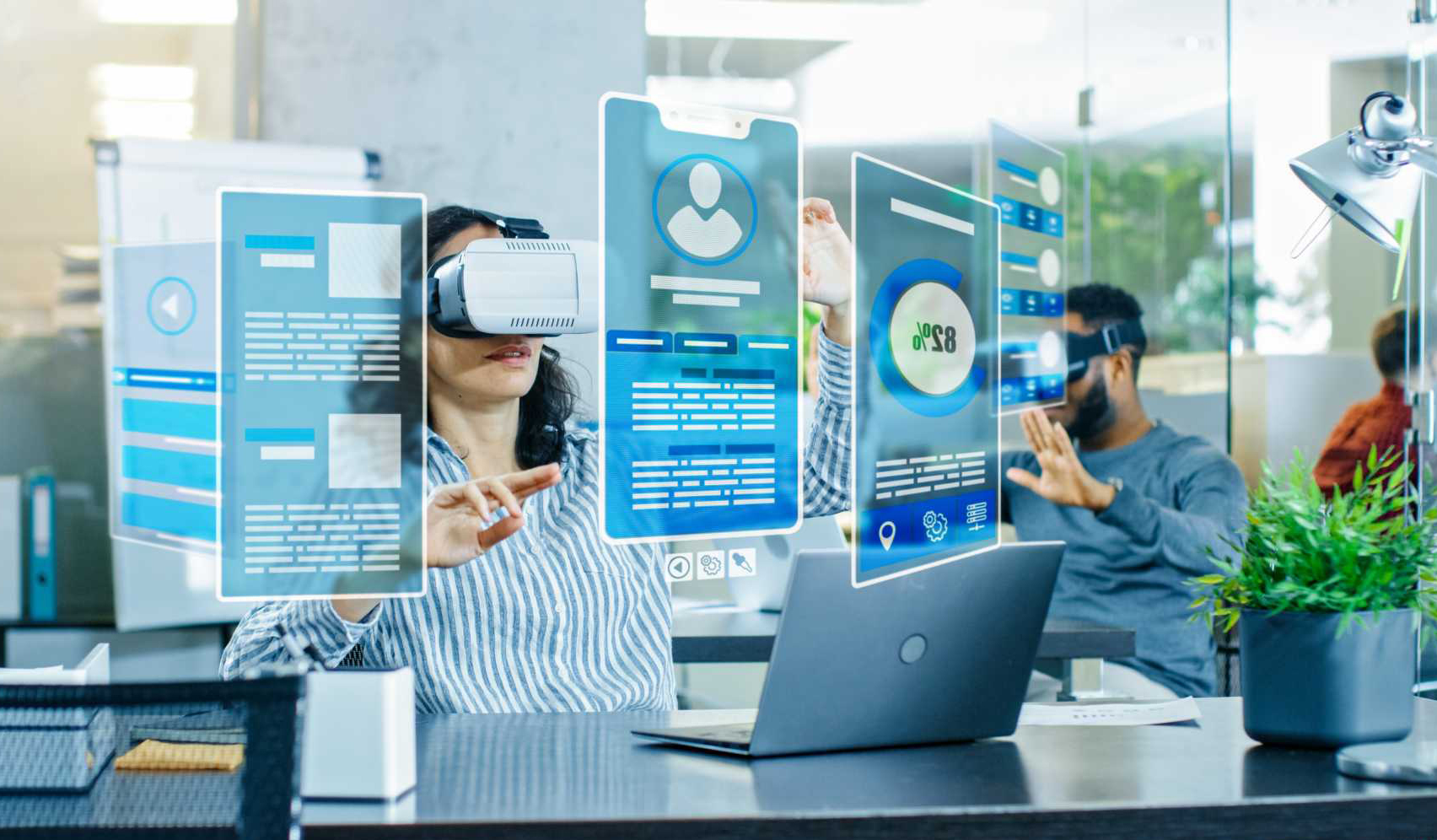

User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design are crucial in virtual reality applications. An effective interface enhances user engagement and satisfaction. For virtual reality training companies, good UI/UX design ensures that users interact with virtual environments intuitively. Poor design can lead to confusion and reduce overall effectiveness. By focusing on usability and accessibility, designers create VR experiences that meet users' needs. Incorporating feedback mechanisms and clear visual cues helps users understand the virtual space more easily. The importance of UI/UX design in VR cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts user adoption and success.
What Sets Virtual Reality UI/UX Apart from Traditional Interfaces
Virtual reality UI/UX design differs significantly from traditional interface design. In VR, users are immersed in a 3D environment, which requires designers to consider spatial relationships and depth. Traditional interfaces rely on flat screens and two-dimensional interactions. In contrast, VR interfaces must account for user movement and orientation in a virtual space. Designing for VR involves new challenges, such as preventing motion sickness and ensuring comfort during prolonged use.
Interactivity in VR is more natural and intuitive. For example, users might reach out to grab virtual objects or move around physically. Traditional interfaces often depend on mouse clicks and keyboard inputs. In VR sports training, athletes can practice movements in a simulated environment that closely mimics real-life scenarios. Such a level of immersion is not possible with traditional interfaces.
Visual feedback and audio cues play a larger role in VR UI/UX design. Designers need to provide clear indications of interactive elements within a 3D space. Additionally, performance optimization is crucial to maintain smooth experiences, as lag or glitches can break immersion. Accessibility considerations are also different, requiring attention to factors like field of view and motion control options. A thorough understanding of these unique aspects is essential for creating effective VR interfaces.
Key Elements That Make or Break VR User Experiences
- Intuitive controls. Users should interact with the virtual environment without confusion or difficulty. Complex control schemes can hinder immersion.
- High-quality graphics. Visual fidelity enhances realism, making the experience more engaging. Poor graphics can break immersion and reduce enjoyment.
- Performance optimization. Smooth frame rates prevent motion sickness and improve user comfort. Lag or stuttering detracts from the overall experience.
- Spatial audio. Accurate sound positioning adds depth to the virtual environment, while inadequate audio can make it feel flat.
- User comfort. Ergonomic design minimizes physical strain during use. Ignoring comfort can lead to fatigue or discomfort.
- Clear feedback mechanisms. Immediate responses to user actions help maintain engagement. A lack of feedback can cause confusion.
- Accessibility options. Features like adjustable text size and control remapping make the experience available to a broader audience. Neglecting accessibility limits the user base.
Focusing on these key elements in VR app development is essential for creating successful applications.
The Impact of Well-Executed UI/UX for VR Apps on User Satisfaction
A well-designed UI/UX in virtual reality significantly boosts user satisfaction. When interfaces are intuitive, users can focus on the content rather than struggling with controls. For example, seamless interactions enhance the sense of presence in the virtual environment.
User satisfaction increases when applications are tailored to meet user needs. Providing customization options allows users to adjust settings to their preferences. This personal touch can lead to longer engagement times. High user satisfaction often results in positive reviews and recommendations. Satisfied users are more likely to share their experiences with others. This word-of-mouth can drive adoption and success for VR applications.
Investing in UI/UX design can lead to better retention rates. Users who enjoy their experience are more likely to return. Repeat usage is essential for applications like VR games or training programs.
Well-executed UI/UX design can also reduce support costs. Fewer user errors and misunderstandings mean less need for customer support. This efficiency benefits both users and developers.
Understanding the Psychological Aspects of VR UI/UX Design
Virtual reality affects users not just physically but psychologically. Designers need to consider how virtual environments influence perception, cognition, and emotion. Understanding these aspects helps in creating experiences that are immersive and comfortable. For instance, too much sensory input can overwhelm users, leading to discomfort. Balancing visual, auditory, and interactive elements is essential. By considering psychological factors, designers can enhance user engagement and satisfaction. Real-world applications, like therapeutic VR programs, show the importance of aligning design with human psychology. A user-centric approach ensures that the virtual experience is not only functional but also emotionally resonant.
Cognitive Load Management in Virtual Environments
Managing cognitive load is critical in virtual reality design. Cognitive load refers to the mental effort required to process information. In VR, users are often presented with complex environments and tasks. Overloading users with too much information can lead to confusion and reduce effectiveness. Designers should aim to simplify interfaces and interactions.
One strategy is to minimize unnecessary visual clutter. Keeping the environment clean and focused helps users concentrate on important elements. Another approach involves providing clear guidance and instructions. For example, using visual cues or prompts can direct users' attention appropriately. Interactive elements should be intuitive and consistent. If users have to learn new controls frequently, cognitive load increases. Standardizing controls across different parts of the application aids in reducing mental effort.
Real-world examples include VR training programs where simplicity enhances learning outcomes. By carefully managing the amount of information presented, users can absorb material more effectively. Techniques like progressive disclosure, where information is revealed gradually, can be beneficial. Considering the limitations of human memory and attention span is also important. Designers should avoid requiring users to remember complex sequences or numerous steps. Providing immediate feedback helps users understand the consequences of their actions without additional cognitive strain.
Designing for the Brain: How to Engage Users on a Deeper Level
Engaging users in virtual reality requires understanding how the brain processes experiences. Designers can tap into psychological principles to create more compelling interactions. One method is to use storytelling elements within the VR environment. Narratives can make experiences more memorable and emotionally impactful.
Another aspect is leveraging the sense of presence. When users feel truly immersed, they are more likely to engage deeply. Techniques like realistic environments and responsive interactions enhance this feeling. For instance, in VR simulations for education, realistic scenarios can improve learning by making it more relatable.
Emotional design also plays a role. Incorporating elements that evoke emotions can strengthen user engagement. Colors, sounds, and visuals can be used strategically to influence mood. For example, calming colors and sounds can make a meditation app more effective.
Personalization is another powerful tool. Allowing users to customize aspects of the VR experience can increase their connection to it. This could include avatar customization or choosing preferred settings. Personalized experiences feel more relevant and engaging. Social interaction within VR can also deepen engagement. Features that enable users to interact with others add a layer of connectivity. Multiplayer VR games or collaborative workspaces benefit from this approach.
By designing with the brain in mind, VR experiences become more than just visual simulations. They transform into meaningful interactions that resonate with users on a deeper level. Understanding psychological principles allows designers to create VR applications that are not only functional but also emotionally engaging.
Best Practices for Crafting Effective Virtual Reality Apps UX
Developing a successful virtual reality user experience involves adhering to specific design principles. Emphasizing user comfort and intuitive interactions is paramount. For instance, incorporating familiar gestures can make the virtual environment more accessible. Consistency in design elements also helps users feel more at ease. Real-world applications show that attention to detail in UI/UX design enhances overall user satisfaction. By focusing on these best practices, developers can create VR experiences that are both engaging and user-friendly.
Minimizing Friction in Complex VR Systems
Reducing friction in virtual reality systems improves user engagement and satisfaction. Complex interfaces can overwhelm users, so simplifying interactions is essential. Here are key strategies:
- Simplify controls. Making input methods straightforward enhances usability.
- Optimize performance. Ensuring smooth operation prevents technical hiccups.
- Provide clear feedback. Immediate responses to actions keep users informed.
- Streamline navigation. Easy movement within the environment reduces confusion.
- Limit distractions. Minimizing unnecessary elements keeps users focused.
Incorporating these practices can make even complex VR systems more approachable. For example, virtual reality therapy applications benefit from reduced friction by allowing patients to concentrate on treatment without technical barriers. Overall, minimizing friction leads to a more seamless and enjoyable user experience.
Utilizing Visual Cues for Intuitive Navigation
Visual cues play a crucial role in guiding users through virtual environments. Effective use of these cues can make navigation more intuitive. Consider the following techniques:
- Highlight interactive elements. Making actionable items stand out encourages interaction.
- Use consistent symbols. Familiar icons help users recognize functions quickly.
- Employ directional indicators. Visual guides point users toward objectives.
- Adjust lighting strategically. Lighting can draw attention to important areas.
- Apply color coding. Different colors can signify various functions or zones.
By implementing these visual strategies, users can navigate VR spaces more easily. This approach reduces the learning curve and enhances the overall experience. Games and educational VR applications often use visual cues effectively to keep users engaged and oriented within the virtual world.
Achieving Balance Between Minimalism and Functionality in VR Design
Striking the right balance between simplicity and functionality is vital in VR design. Too much minimalism can lead to a lack of necessary features, while excessive complexity can overwhelm users. Here are some guidelines:
- Focus on essential features. Prioritize elements that serve the primary purpose.
- Avoid clutter. Removing unnecessary items keeps the interface clean.
- Ensure accessibility. Design with all users in mind, including those with limitations.
- Allow customization. Giving users control over specific settings enhances satisfaction.
- Maintain consistency. Uniform design elements reduce confusion.
Achieving this balance makes VR applications more effective and user-friendly. For instance, in virtual reality therapy, a well-balanced design ensures that therapeutic content is delivered efficiently without overwhelming the patient. By carefully considering both minimalism and functionality, designers can create VR experiences that are both simple and rich in features.
Designing UI for VR Apps for Better User Comfort


Orbis VR App
User comfort is a critical aspect of virtual reality design. Poorly designed interfaces can lead to discomfort or motion sickness. Focusing on ergonomic principles helps create comfortable VR experiences. For example, positioning interactive elements within easy reach reduces physical strain. Adjusting visual elements to match natural human perception also enhances comfort. Considering factors like field of view and movement speed can prevent disorientation. Developers improve overall satisfaction and usability by prioritizing user comfort in UI design.
Tackling VR Sickness Through Smart UI/UX Decisions
VR sickness is a common issue that can hinder the enjoyment of virtual reality experiences. Smart UI/UX design choices can mitigate this problem. One effective strategy is to reduce the latency between user actions and system responses. Lower latency minimizes the disconnect between visual input and physical motion. Another approach involves limiting rapid or unexpected movements within the virtual environment. For instance, smooth and predictable motion paths can enhance comfort in VR entertainment applications.
Adjusting the field of view can also help reduce VR sickness. A narrower field of view can decrease the sensation of motion. Providing users with control over movement, such as allowing teleportation instead of continuous motion, can further alleviate discomfort. Incorporating stationary reference points within the environment helps maintain a sense of balance.
Audio cues synchronized with visual elements can enhance spatial awareness and reduce disorientation. Avoiding high-contrast visual patterns that strain the eyes is also beneficial. Regular reminders for users to take breaks can prevent fatigue. By implementing these smart UI/UX decisions, developers can create VR experiences that are more comfortable and accessible to a wider audience.
Ensuring Smooth Transitions Between Virtual Spaces
Seamless transitions are essential for maintaining immersion in virtual reality. Abrupt changes between scenes can cause confusion or discomfort. Designing smooth transitions helps users stay engaged. One method is to use fade effects when moving from one environment to another. Gradual changes in visuals and audio can ease the user into the new space.
Another technique involves using portals or doorways within the virtual environment. This provides a logical and intuitive way to move between spaces. Consistent visual cues and themes across different areas can aid in reducing the cognitive load during transitions. For example, maintaining similar lighting or color schemes helps users adjust more quickly.
Implementing interactive elements during transitions can keep users engaged. For instance, a brief interactive task or animation can distract from the loading process. Ensuring that transitions do not require complex user actions prevents unnecessary confusion. Testing transitions with real users can provide valuable feedback for improvement.
Optimizing performance is also crucial. Lag or delays during transitions can break immersion. By preloading assets or using efficient coding practices, developers can minimize these issues. Smooth transitions contribute significantly to the overall user experience in VR applications.
UI/UX Testing and Iteration — The Roadmap to Success
Testing and iteration are essential in developing effective virtual reality applications. Continuously refining UI/UX designs leads to better user experiences. Early testing helps identify issues like user discomfort or confusing interfaces. By addressing these problems promptly, developers enhance the application's usability. Iterative design allows for adjustments based on real user feedback, resulting in a more polished product. Successful VR projects often undergo multiple rounds of testing and improvement. This process ensures that the final application meets user expectations and performs smoothly.
Why Rapid Prototyping Is Critical for VR Projects
Rapid prototyping accelerates the development of virtual reality applications. Creating quick prototypes allows developers to test ideas early. This approach identifies potential issues before investing significant time and resources. For example, a basic VR environment can reveal whether users find the navigation intuitive, enabling adjustments to improve the design.
Early prototypes also help in gathering user feedback. Real users interacting with the prototype provide valuable insights. Their reactions highlight what works well and what needs improvement, guiding the development team in refining the application. Another benefit of rapid prototyping is cost efficiency. Identifying flaws early reduces expenses associated with late-stage changes, making the development cycle more efficient and saving both time and money.
Collaboration among team members improves with prototypes. Visual representations of ideas make communication clearer. Designers, developers, and stakeholders can align their visions more effectively. In virtual reality projects, where user experience is paramount, rapid prototyping ensures that the final product meets user needs. Testing concepts quickly allows teams to innovate and deliver high-quality VR applications.
Incorporating User Feedback into the Design Process
User feedback is vital in designing successful virtual reality applications. Engaging with users throughout development provides insights that might not be apparent to the team. For instance, users may encounter challenges that designers did not anticipate.
Feedback can be collected through user testing sessions. Observing how users interact with the VR application reveals areas needing improvement. Surveys and interviews offer additional perspectives on user satisfaction and preferences.
Incorporating this feedback leads to a more user-centric design. Adjustments based on user input enhance usability and enjoyment. If users report difficulty with controls, developers can modify the interface to be more intuitive.
Regularly integrating feedback keeps development aligned with user expectations. It prevents the accumulation of issues that could become problematic later, making the end product more polished and tailored to the target audience.
Real-world examples show that applications incorporating user feedback perform better in the market. Users feel valued when their opinions influence the final product, building a loyal user base and improving the application's reputation.
Tools for Effective UI/UX Testing in Virtual Reality
Various tools assist developers in testing and refining UI/UX in virtual reality applications. Utilizing the right tools enhances the efficiency of the testing process. Here are some popular options:
- Unity and Unreal Engine Testing Frameworks. These game engines offer built-in tools for prototyping and testing VR experiences. Developers can simulate user interactions and identify issues early.
- VR Analytics Platforms. Tools like Cognitive3D provide analytics on user behavior within VR applications. Data on where users look and how they interact helps optimize the experience.
- UserTesting for VR. Services that facilitate user testing sessions allow developers to gather real user feedback. Observing users in controlled environments reveals practical insights.
- Bug Tracking Software. Applications like Jira help manage and track issues found during testing. Organizing bugs and feedback ensures problems are addressed systematically.
- Eye-Tracking Tools. Devices that monitor where users focus their gaze provide information on interface effectiveness. Adjustments can guide user attention appropriately.
- Motion Capture Systems. Recording user movements helps understand how people interact physically with the VR environment. This data aids in refining controls and interactions.
Selecting appropriate tools depends on the project's specific needs and resources. Combining several tools often yields the best results. Effective testing leads to a more polished and user-friendly VR application. Incorporating these tools into development enhances the quality of the final product. Developers can identify and fix issues more efficiently, which ultimately leads to better user satisfaction and market success.
Future Trends in the Design of Virtual Reality User Experience
Advancements in technology are shaping the future of virtual reality user experience design. Emerging trends focus on making VR more immersive and accessible. For example, developers are exploring integrating artificial intelligence to create more responsive environments. Additionally, the incorporation of haptic feedback enhances the tactile aspect of VR. Cross-platform compatibility is also gaining attention, allowing users to access VR content on various devices. Real-world applications, such as virtual reality therapy, are benefiting from these developments. By staying updated with these trends, designers can create VR experiences that are more engaging and user-friendly.
AI-Powered Interfaces and Adaptive UI for VR
Artificial intelligence is playing a significant role in advancing virtual reality interfaces. AI-powered systems can adapt the user interface based on individual preferences and behaviors. For instance, machine learning algorithms analyze user interactions to customize the layout and controls. This personalization enhances usability and makes the experience more intuitive. In VR gaming, AI can adjust difficulty levels in real time to match the user's skill. Adaptive UI also benefits applications like virtual reality therapy by tailoring content to meet specific therapeutic needs.
Integrating voice recognition and natural language processing allows for more natural interactions within the VR environment. Chatbots and virtual assistants can guide users, providing support and information as needed. These AI-driven features reduce the learning curve and make VR more accessible to newcomers. Security and privacy considerations are important when implementing AI in VR. Ensuring that user data is protected builds trust and encourages adoption. Overall, AI-powered interfaces are transforming how users interact with virtual reality, making experiences more personalized and engaging.
The Rise of Multimodal Interfaces Beyond Visuals
Virtual reality is expanding beyond visual experiences to include other senses. Multimodal interfaces integrate audio, touch, and smell to create more immersive environments. Haptic feedback devices provide tactile sensations, allowing users to feel virtual objects. For example, gloves equipped with sensors simulate the texture and resistance of materials. In VR entertainment, this technology enhances realism and engagement.
Audio plays a crucial role in immersion as well. Spatial audio techniques create a three-dimensional soundscape, improving the user's sense of presence. Voice commands offer an alternative method of interaction, making controls more intuitive. Some VR systems experiment with olfactory feedback, introducing scents to the virtual environment. This addition can make experiences like virtual tourism more authentic.
Eye-tracking technology is another component of multimodal interfaces. By monitoring where users look, systems can adjust focus and depth of field dynamically. This technology also enables foveated rendering, improving performance by reducing detail in peripheral vision areas. Combining these modalities leads to more prosperous and more engaging VR experiences. Designers need to consider how these elements work together to create cohesive interactions. Multimodal interfaces represent a significant step forward in virtual reality, offering users a more complete and immersive experience.
Smoother User Experience for Your VR Apps with Program-Ace
Program-Ace offers extensive expertise in developing high-quality virtual reality applications. Our team focuses on creating user-friendly interfaces that enhance engagement and satisfaction. As a leading software development service provider, we have completed VR projects across various industries, including gaming, education, and healthcare. Clients benefit from our commitment to understanding their requirements, ensuring that the final product aligns perfectly with their goals.
We utilize the latest technologies and best practices to optimize performance and user experience. Our developers prioritize usability and accessibility, making applications intuitive for all users. By partnering with us, clients gain access to a dedicated team that provides support throughout the entire development process, from initial concept to final deployment.
Real-world examples highlight our ability to deliver effective VR solutions. For instance, we helped an educational institution create an immersive learning platform that improved student engagement. In the healthcare sector, we developed a virtual reality therapy application that aided patients in rehabilitation. Our approach combines technical proficiency with a strong focus on user satisfaction and measurable results.
Feel free to contact us and learn more about how we can assist with your VR project. We are prepared to work with you to realize your VR dreams.
























