Did you know that 48% of US consumers have had at least one virtual reality experience? This statistic is more than just a number; it represents a significant shift in the technological landscape, where augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are no longer futuristic concepts but present-day realities. As these technologies continue to evolve and integrate into various sectors, businesses are faced with a critical dilemma: virtual reality vs augmented reality.
In this article, Program-Ace, as a VR/AR development company, aims to demystify these technologies, offering a comprehensive understanding of their workings, benefits, risks, and potential future developments. By comparing and contrasting AR and VR, we will explore their unique features and provide practical examples to illustrate their differences.
Whether you are a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or simply curious about the future of technology, this guide will help you navigate the exciting world of AR and VR, empowering you to make informed decisions in this rapidly evolving digital era.
The Rise of AR & VR: Brief Overview
The history of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) is a fascinating journey marked by groundbreaking innovations and the involvement of major market players who have pushed the boundaries of what's possible in technology. This evolution has transformed AR and VR from mere concepts into integral parts of our digital experience.
The story of VR begins in the 1960s with Morton Heilig's Sensorama, an early VR machine, and Ivan Sutherland's creation of the first VR head-mounted display system, known as The Sword of Damocles, in 1968. These were the foundational steps in VR, setting the stage for what was to come.
AR's roots can be traced back to 1968 as well, with Sutherland's head-mounted display being a precursor. However, it was only in the 1990s that AR started to take shape as a distinct technology, particularly with Tom Caudell coining the term "Augmented Reality" while working at Boeing to describe a digital display system designed to assist in aircraft manufacturing.
The 1990s and 2000s saw significant contributions from various companies and institutions that propelled AR and VR forward. In the realm of VR, companies like Nintendo and Sega were early players, experimenting with VR in gaming. Nintendo’s Virtual Boy, a tabletop portable console with a head-mounted display, although not successful, was a notable early attempt at bringing VR to the consumer market.
In the field of AR, the late 1990s and early 2000s witnessed several academic and military applications. However, it was the advent of smartphones with advanced computing capabilities, cameras, and sensors that truly unlocked the potential of AR for mass consumption.
The 2010s marked a turning point for both AR and VR, with major tech companies entering the arena. In VR, the launch of Oculus Rift in 2012, initially a Kickstarter project by Palmer Luckey, was a game-changer. The subsequent acquisition of Oculus VR by Facebook in 2014 for $2 billion signaled the industry's potential. This move was followed by other tech giants like Sony with PlayStation VR, HTC with the Vive, and Valve with the SteamVR platform.
In AR, the release of Google Glass in 2013, although not a commercial success, was pivotal in bringing AR into public consciousness. Microsoft’s HoloLens, introduced in 2016, took AR a step further by offering a more refined and powerful mixed-reality experience. Meanwhile, the launch of ARKit by Apple and ARCore by Google enabled millions of smartphone users to experience AR, further solidifying its presence in the consumer market.
The explosion of mobile AR, driven by ARKit and ARCore, has been instrumental in AR's growth. Popular apps like Pokémon GO and Snapchat filters have introduced AR to a broad audience, showcasing its potential for entertainment, social media, and beyond.
Significance of AR and VR in Modern Technology Landscape
AR and VR technologies are not just fleeting trends in the modern technology landscape; they represent a significant and rapidly expanding market. The projected revenue for the AR & VR market stands at an impressive $32.1 billion in 2023. This figure is more than a testament to their growing popularity; it's an indicator of their transformative impact across various sectors.
The AR and VR market is expected to grow at an annual rate of 12.60% (CAGR 2023-2028), culminating in a projected market volume of US$58.1 billion by 2028. This robust growth is fueled by continuous technological advancements and an increasing adoption rate in both consumer and enterprise domains. The user penetration rate, which is projected to be 92.2% in 2023, is expected to surge to 104.9% by 2028.
AR and VR are at the forefront of driving innovation in user engagement. These technologies offer unique, immersive experiences that traditional mediums cannot, making them powerful tools for marketing and entertainment. The gaming industry, in particular, has seen a significant transformation with the introduction of AR and VR, offering gamers an unprecedented level of immersion.
What is Augmented Reality?
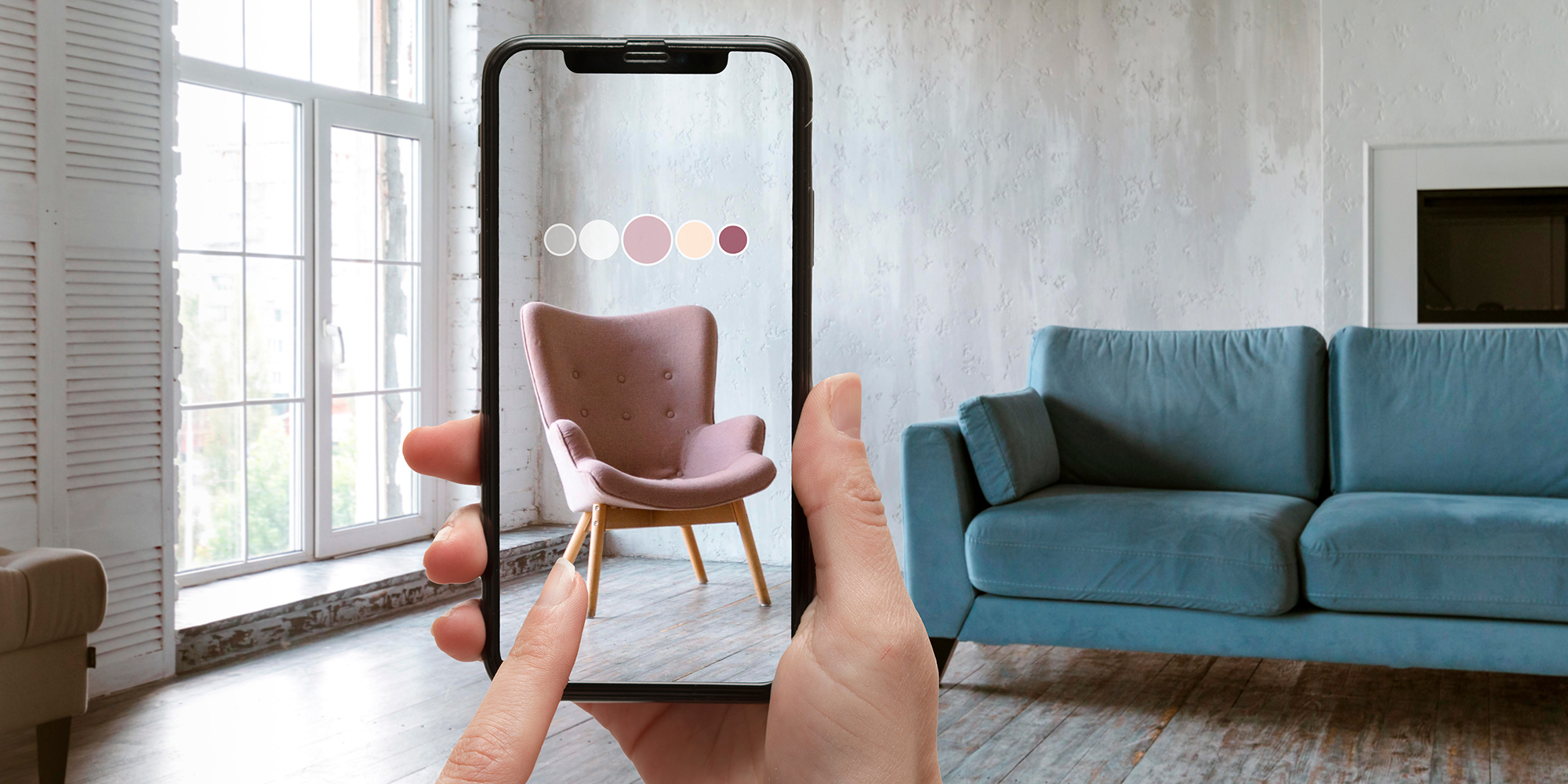

Imagine pointing your smartphone at a magazine page and watching a video play directly on the page, or using an app like Pokémon GO, where digital creatures seem to inhabit the real world around you. These are examples of AR, a technology that overlays digital information onto the physical world, enhancing our perception of reality.
AR is a technology that superimposes computer-generated images, sounds, or other data onto the real world, creating a composite view that augments the natural environment. Unlike VR, which creates a completely artificial environment, AR enhances the real world with digital details that can be interacted with in real-time.
How Does Augmented Reality (AR) Work?
- Device with a Camera and Sensor. AR typically requires a device equipped with a camera, such as a smartphone, tablet, or AR glasses. These devices capture the real-world environment.
- Processing and Projection. The AR device processes the input from its camera, interpreting the physical space and its dimensions. It then projects digital content, such as images or animations, onto this space.
- Real-Time Interaction. Augmented reality allows for real-time interaction with both real and virtual environments, often using gestures or screen touches for manipulation and expanding the users’ experience.
- Context-Awareness. Advanced AR systems are context-aware, meaning they recognize the environment and adjust the digital overlay accordingly, ensuring a seamless blend between the real and the virtual.
Benefits and Risks of AR
As you can see, leveraging augmented reality brings a set of advantages to businesses in various industries, for example:
- Enhanced Learning and Training. AR can provide interactive, immersive educational experiences, making learning more engaging.
- Improved Shopping Experience. In retail, AR allows customers to try products virtually before buying.
- Innovative Marketing. AR offers unique, engaging ways for brands to connect with audiences and attract consumers.
- Enhanced Navigation. AR can overlay directions onto the real world, simplifying navigation in unfamiliar environments.
- Medical and Healthcare Advancements. AR is used for advanced surgical training and patient care visualization.
- Maintenance and Repair. In industries, AR can assist technicians by overlaying repair instructions onto equipment.
At the same time, AR is associated with several risks, namely:
- Privacy Concerns. AR applications may access sensitive personal data, raising privacy issues.
- Security Vulnerabilities. Like any technology, AR systems can be susceptible to hacking and data breaches.
- Over-Reliance on Technology. Excessive dependence on AR for daily tasks may diminish users' real-world skills and spatial awareness.
- Potential for Distraction. AR applications, especially in mobile devices, can be distracting and potentially dangerous in situations like driving.
- Health Effects. Prolonged use of AR devices may lead to eye strain or headaches.
- Technical Limitations. Current AR technology may have limitations in accuracy and real-time processing, affecting user experience.
What Is Virtual Reality?
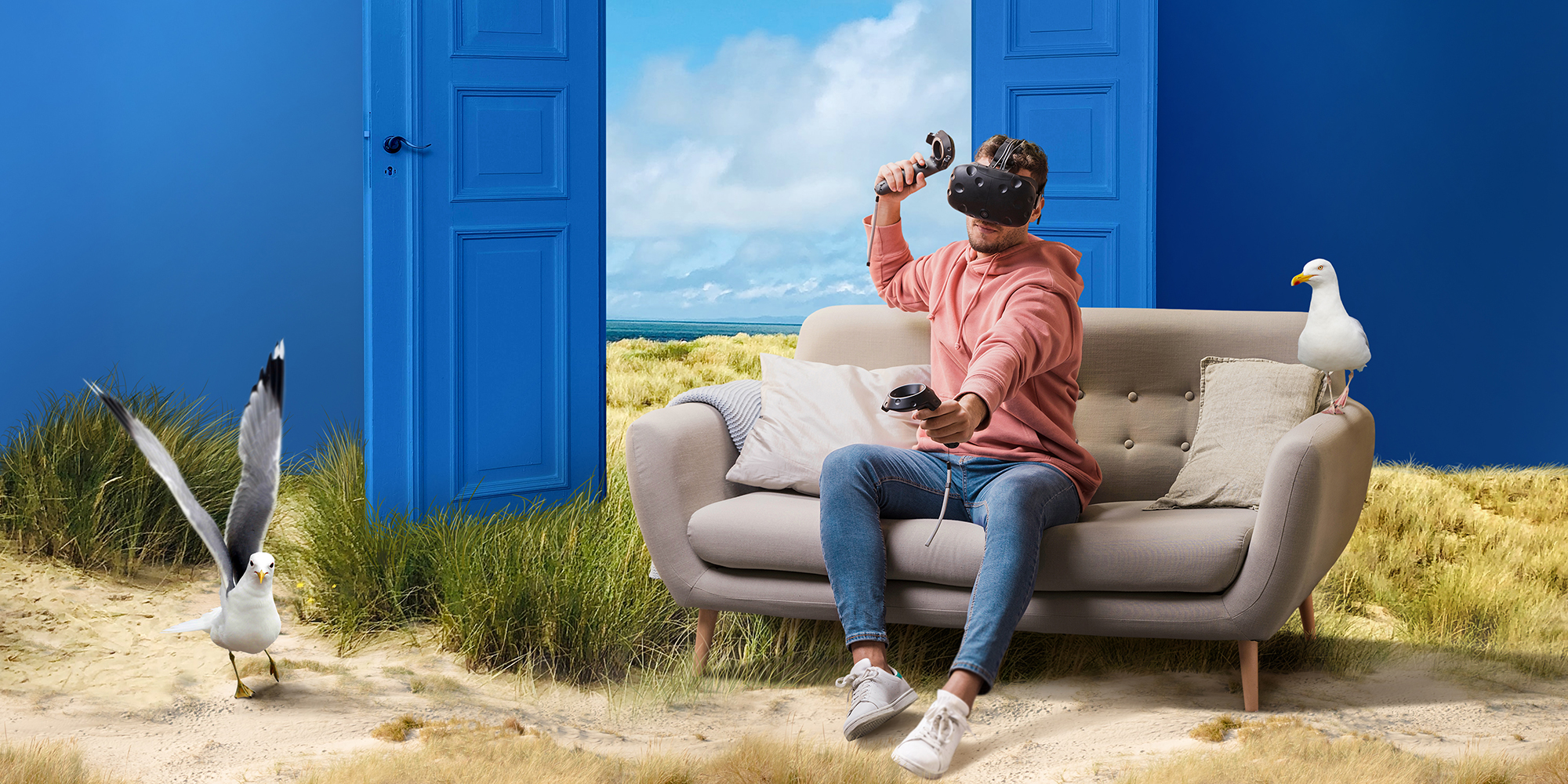

Have you ever dreamt about traveling to a virtual concert where you're standing next to a lifelike avatar of your favorite artist, or fighting Dart Vader with a lightsaber? These experiences are made possible by virtual reality, a technology that completely immerses you in a computer-generated environment.
Virtual reality is a simulated experience that can be similar to or completely different from the real world. It uses computer technology to create a three-dimensional, interactive environment that a person can explore and interact with. VR creates a sense of physical presence in this digital world, often using VR headsets or multi-projected environments.
How Does Virtual Reality (AR) Work?
- VR Headset. The primary tool for experiencing VR is a headset, which covers your eyes and ears, immersing you in a digital environment.
- Motion Tracking. VR headsets often include sensors to track your head, hand, and body movements, allowing the virtual environment to respond in real time to your actions.
- Interactive Controllers. Handheld controllers or gloves can provide tactile feedback and allow you to interact with the virtual environment more naturally.
- High-Quality Graphics and Sound. Advanced graphics and spatial audio are crucial for creating a believable and immersive VR experience.
- Processing Power. VR requires significant processing power to render complex, real-time graphics, often relying on PCs, gaming consoles, or standalone VR devices.
Pros and Cons of VR
So what pushes businesses and other institutions to adopt VR? Let’s review the main advantages of this marvelous technology.

Entertainment and Gaming. VR offers a deeply immersive gaming and entertainment experience, creating new possibilities in digital storytelling.

Therapeutic Uses. VR is used in therapy, including exposure therapy for PTSD and cognitive rehabilitation.

Architectural and Real Estate Visualization. VR allows for the exploration of architectural designs and real estate properties in a realistic way.

Enhanced Remote Collaboration. VR enables more immersive and interactive remote meetings and collaborations.

Innovative Retail Experiences. VR can offer virtual try-ons and tours, enhancing the online shopping experience.
However, it is not all perfect, and certain concerns arise when we are talking about using virtual reality for business purposes.
Cost. High-quality VR systems can be expensive and require a lot of resources to work properly, limiting the technology accessibility.

Isolation. Prolonged use of VR can lead to a sense of isolation from the real world, creating issues for users with social interactions.

Motion Sickness. VR can cause disorientation or motion sickness in some users, known as VR-induced nausea.

Hardware Requirements. Demanding hardware requirements for high-end VR systems can be a barrier.

Limited Content. The availability of high-quality VR content is still growing and may not appeal to all users.

Physical Space Requirements. Using VR often requires a certain amount of physical space, which can be a limitation for users.
AR vs VR: The Main Differences
Have you ever wondered what is the crucial difference between AR and VR? While both technologies are reshaping our interaction with the digital world, they offer distinctly different experiences and applications. Let's break down the topic of VR vs AR in a comparison table to understand them better.
| Aspect | Augmented Reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
| Definition | AR overlays digital information in the real-world environment. | VR creates a completely immersive digital environment, isolated from the real world. |
| User Experience | Enhances the real world with digital elements. | Transports the user to a completely different environment. |
| Interaction with Environment | Interacts with both digital elements and the real world. | Interaction is limited to the virtual environment. |
| Hardware | Requires devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses. | Utilizes headsets like Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, or PlayStation VR. |
| Applications | Used in navigation, educational content, shopping, and interactive marketing. | Popular in gaming, immersive training, metaverse, virtual tours, and therapeutic uses. |
| Immersion Level | Partial immersion, maintaining awareness of the real world. | Full immersion, often losing all contact with the real world. |
| Portability | Generally more portable and accessible, as many AR apps work on smartphones and tablets. | Less portable, often requiring dedicated space and a more complex setup. |
| Development Complexity | Less complex as it integrates with the real world and requires less content creation. | More complex due to the need to create entire environments and detailed graphics. |
| Cost | Often lower cost due to the use of existing devices like smartphones. | Can be higher due to the need for specialized hardware and more complex software. |
Understanding the difference between VR and AR is essential for businesses and developers when deciding which technology to invest in or integrate into their products and services. AR offers a more accessible and less immersive experience, enhancing the real world with digital elements, while VR provides a fully immersive experience, creating entirely new digital environments. Each has its unique strengths and is suited to different applications and user experiences.
Augmented Reality Vs Virtual Reality: Examples of the Difference

To illustrate the difference between augmented reality and virtual reality in detail, let's explore four pairs of apps from around the world, each pair containing one AR app and one VR app. These examples will highlight how each technology is used in different contexts.
IKEA Place (AR): This app allows users to visualize how furniture from IKEA would look in their own homes. By using the camera on a smartphone or tablet, users can place true-to-scale 3D models of furniture in their rooms. This app demonstrates AR's ability to blend digital objects with the real world for practical purposes like interior design.
Oculus Home (VR): A VR application where users can create and customize their own virtual living space in a fully immersive environment. In Oculus Home, users can design interiors with virtual items and experience them as if they were actually inside this digital space, showcasing VR's capability to create and interact with entirely virtual worlds.
Snapchat Filters (AR): Snapchat uses AR technology to apply real-time special effects and sounds to photos or videos. Users can overlay digital elements such as animal ears or glasses onto their faces, which track and move with their facial movements. This app highlights AR's ability to enhance real-world imagery with fun and interactive digital overlays.
Google Earth VR (VR): This application allows users to explore a virtual representation of the entire globe. Users can virtually visit different places, experiencing immersive 3D landscapes and cityscapes. Unlike AR apps, Google Earth VR users are completely immersed in a digital environment, detached from their physical surroundings.
Google Lens (AR): Google Lens is an AR app that allows users to use their smartphone camera to identify objects, text, and landmarks in the real world. By pointing the camera at different items, users can get information, translate text, or even see how products would look in their space. This app exemplifies AR's capability to provide real-time information overlaid on the physical world.
Tilt Brush (VR): Tilt Brush by Google is a VR app that lets users paint in three-dimensional space with virtual reality. In a completely immersive environment, users can create, manipulate, and experience art in a way that's impossible in the physical world. This app showcases VR's ability to create entirely new spaces for creative expression, unbound by the constraints of the real world.
OishiiAirEating (AR): This AR application is designed for entertainment and cultural promotion. Using AR technology, allows users to take pictures or videos with various effects related to Japanese culture. The app uses facial recognition and tracking to overlay these digital elements onto the user's environment, enhancing their real-world surroundings with culturally themed filters.
Hand Rehabilitation Training (VR): This VR application takes a practical approach to rehabilitation. Built for the Oculus Quest VR platform, it places users in a digital setting where they interact with a virtual trainer to complete exercises aimed at improving hand mobility and strength. The app uses advanced motion tracking to monitor and guide the user's hand movements with high precision.
What Can We Expect From AR And VR In The Future?
As we look towards the future, AR and VR are poised to evolve in exciting ways. Four main trends are likely to shape the trajectory of these technologies, impacting various sectors and changing the way we interact with the digital world.
Enhanced Integration in Daily Life
AR and VR are expected to become more seamlessly integrated into our daily lives. For AR, this means more interactive and context-aware applications in smartphones, wearable devices, and even in-car windshields, enhancing everyday activities like navigation, shopping, and education. VR, on the other hand, is likely to expand beyond gaming and entertainment, becoming a regular part of home entertainment systems, offering immersive experiences in watching movies, attending virtual concerts, or even socializing in virtual spaces.
Advancements in Technology and Accessibility
Technological advancements will continue to drive AR and VR forward, making them more accessible and affordable. We can expect to see lighter, more comfortable, and higher-resolution headsets for VR, along with more advanced motion tracking and haptic feedback systems. For AR, advancements in mobile computing power, camera technology, and AI will lead to more sophisticated and realistic overlays of the real world. These improvements will not only enhance the user experience but also make these technologies more accessible to a broader audience.
Expansion in Business and Education
Both AR and VR will see significant expansion in business and educational applications. In business, AR can be used for product demonstrations, interactive marketing, and enhancing customer experiences, while VR can be utilized for virtual meetings, employee training, and simulations. In education, these technologies will revolutionize learning by providing immersive and interactive experiences that can simulate real-world scenarios, making learning more engaging and effective.
Breakthroughs in Healthcare and Therapy
The healthcare sector is set to benefit greatly from AR and VR. AR will find increased use in assisting surgeries, medical training, and patient care, providing real-time data and imagery to healthcare professionals. VR's potential in therapy and rehabilitation will also be more fully realized. It will be used for treating conditions like PTSD, anxiety disorders, and phobias, as well as in physical rehabilitation programs, offering safe and controlled environments for patients to practice and recover.
Enter the World of AR/VR with Program-Ace
Augmented and virtual reality can bring a lot to your company, but to truly understand their potential, you need a strong technical backup. Program-Ace, a leading software development company, knows how to harness the power of virtual worlds for the benefit of businesses in any industry. Feel free to contact us and learn the details.
























