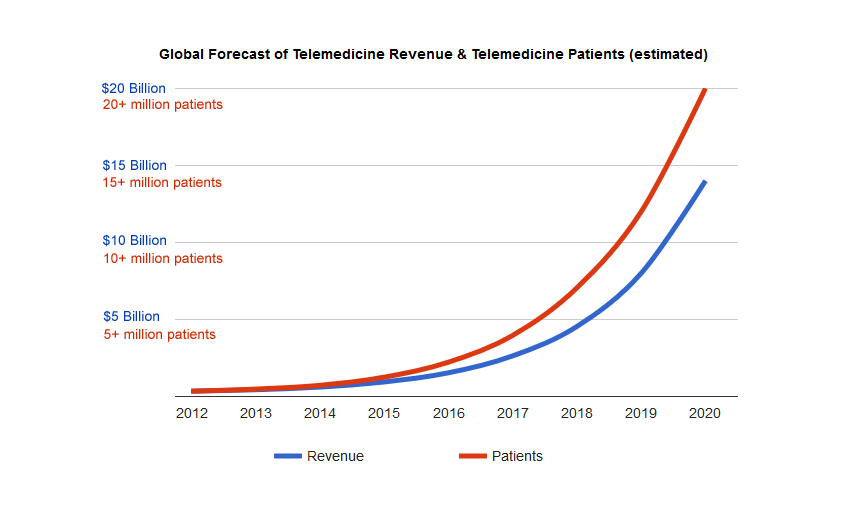
If 2020 has taught us anything, it is that so many tasks and errands that we thought required travel and physical presence can be done remotely. Millions of people are not only working from home, but also shopping from home, learning from home, and even exercising from home. Medical care is no exception to this trend.
In fact, more than 3 out of every 4 hospitals in the U.S.A. already use remote patient monitoring or similar healthtech solutions. There has never been a better time to develop a telemedicine program, and we want to cover everything you need to know before you go down this road.
Looking for healthcare development services? We are ready to help!
What is Telemedicine?
In the strict sense of the word, telemedicine is the practice of using technology to provide treatment to patients at a distance. But how does telemedicine work? It does not involve shipping medicine and administering it via robots, but rather providing guidance and consultation to patients without them needing to visit a doctor or hospital.
Nevertheless, most of the time when people mention telemedicine, they use it as a synonym of telehealth. Telehealth also refers to various remote health services, but is not limited to treatment and extends to health training and education, staff communication and organization, hospital administration, and a range of other fields.
To prevent any confusion, let’s think of telemedicine as any healthcare services provided remotely with technology.
You might think that telemedicine is an invention of the modern age, but in fact, it has been around for centuries, from the time of the earliest communication technologies like mail delivery, telegraph, and telephone. As there are many more technologies available today, there are also more branches and associated practices of telemedicine. For example, mHealth refers to health services accessed and provided via mobile devices, while EMR (electronic medical record) is a system of storing patients’ health records and related information.
Where is Telemedicine Software Used?
Before you begin developing your app, you should consider where it will be used. Smartphones and PCs are the two most common devices for such apps, and with good reason. In this day and age, over half of the population of most countries owns a smartphone and/or personal computer, so these devices make for great development targets. Smartphones have the advantage of being accessible wherever you go, while computers can run powerful programs and provide visual information on a big screen.
However, the two aforementioned devices are hardly the limit when it comes to the implementation of such apps. Firstly, you have gadgets like tablets and media players that have the same mobility perk. Additionally, you have wearable devices (wearables) like smartwatches and fitness trackers with some wellness monitoring features built-in. Moving past the traditional choices, we can also find custom apps developed for smart TVs (featuring recommendatory clips and media), smart homes and virtual assistants (monitoring physical and mental conditions and identifying hazards), and even cars (measuring biometrics and detecting serious issues). New devices are being invented every year and harnessing the advantages of telemedicine, so our list is hardly exhaustive.
Who Will Use the Telemedicine App?
Another important question to consider is who your app will be tailored to. Since children are not old enough to make informed health decisions or fully comprehend most health recommendations, you will likely target adults. If you anticipate your app being used mostly by elderly folks or people with a specific illness, you may need to adapt it to be accessible to patients of this category, e.g. making text in the app large and easy to read for those with poor eyesight. Finally, you should consider that not all people and areas have access to the internet, so adding some features of telemedicine that require no network can be helpful.
Common Types of Telemedicine Apps
Looking at the existing spectrum of apps available can give you a good understanding of the state of the market and what people are actually using, not to mention possibly serving as an inspiration to your future app. We have narrowed down the main types of apps to 5, though they could just as well be called features.
1. Medical data organization
Since we entered the digital era, it has become much more convenient to store records and data digitally than on pages and files that take up physical space. Accordingly, many hospitals, clinics, and other centers involved in collecting medical information are using software to save and organize patient records and data.
2. Communication
One of the objectives that telemedicine seeks to achieve is eliminating the need of patients to visit a hospital to get a checkup or consultation. Thus, doctors and other practitioners looking to the future are experimenting with using communication apps to help patients remotely and give them accurate and helpful information. These apps are also being used for communication between medical workers, students, and interns.
3. Monitoring and diagnosis
Applications of this kind are geared towards monitoring a person’s condition and detecting issues. When issues are detected, the software can often help with diagnosis or point you to someone who should be able to conduct diagnosis and administer treatment. Sometimes, these apps rely on self-reporting (inputting information into the system) to provide a data-driven response, while others rely on collecting data from various sensors, including pulse checkers, motion detectors, and cognitive exercises.
4. Scheduling
Traditionally, people set up doctor’s appointments by calling in to the hospital and waiting for the receptionist to find a suitable timeslot. Software makes the process easier and faster, eliminating the need to call or involve a receptionist – the program can do everything to set up an appointment for you, and you just need to make a selection of data and time along with adding a few details. This kind of software can also be used for several other scheduling practices, such as reminding people to take medicine at a certain time or informing about interesting medical events taking place soon.
5. Guidance
Sometimes, users are just looking for information about illness and wellness and don’t want to travel to a hospital to get it. This is where informational and guidance apps come in. They provide important information about illnesses and how they are treated, along with tips and instructions for staying healthy. For example, WebMD and Mayoclinic – two very popular medical websites, have developed proprietary apps for providing users with helpful information on their mobile devices.
While these categories apply to most Telemedicine apps, they hardly cover all of them. Furthermore, these categories are not necessarily exclusive in an app, and it is perfectly normal for a program to include broad functionality combining several such features. MoMedX is a good example of such an application. It was developed by Program-Ace, and is packed with features: providing guidance to nurses, helping patients and hospital staff communicate, facilitating the scheduling of appointments, and much more.
What do You Need to Develop a Telemedicine App?
App development usually begins with an idea and vision, which is slowly transformed into something more tangible and concrete. First and foremost, you will need expert developers. They should be familiar with the platforms that the application will run on and be able to write clean and efficient code that will implement needed features.
Designers and 2D/3D artists are also crucial personnel for your project, since your program will need a user interface, backend, and possibly artwork/animation to provide a certain experience to the user. While it is possible to learn both coding and design independently, it takes a long time to become good at them, and this is a lot of work for one person to take on. Thus, it is recommended to hire a team of developers and designers, which may also include project managers, QA engineers, and several other categories of specialists.
Testing is an essential practice in software development, so you will need proper hardware to test the program that you build, and to build it in the first place. Most developers use laptops and PCs in their work, while testing hardware can be mobile phones, wearable gadgets, smart TVs, and whatever other platforms you gear your product toward. If your program will have a backend or network connection capabilities, you will also need a hosting service and possibly cloud computing solutions.
Software is also important to mention in the context of development requirements, as every IT profession has an assortment of programs that they use every day in their work. Developers have IDEs (integrated development environments), artists have design and modeling software, PMs and QA engineers also have their own professional tools.
Finally, it is important to mention relevant content. If your application offers any kind of medical and advisory information, its accuracy will be of vital importance. You won’t want people to suffer because of poor advice they received in an app, so your content and information should come from medical professionals and esteemed published works.
Challenges of Telemedicine App Development
Developing any major app for the public is no walk in the park and quite an undertaking, but telemedicine apps in particular have an extra set of challenges that should be overcome. Let’s examine the biggest hurdles in the process:
1. Privacy and confidentiality
There is a big difference between collecting user data from a game where users make individual choices and from a medical application. Medical data is much more sensitive and often confidential, falling under the category of physician-patient privilege. To protect the data of citizens in the digital era, various countries have enacted laws that strictly limit how data can be collected and used.
In the U.S., the main law is HIPAA, while the European Union has GDRP. Subsequently, to prevent your application from being taken down or being taken to court over its data practices, you should ensure full compliance with the data privacy laws of the regions where it will be used.
2. Crafting a viable business strategy
The healthcare app marketplace is incredibly competitive, with hundreds of apps available on the Play Market, App Store, and other marketplaces. Thus, if you are developing software for commercial purposes, you should put a lot of time and thought into your business strategy, consulting with business analysts and studying the existing market. If the product will be offered free of charge, you will probably not have these concerns, though you should still consider how helpful and convenient this solution will be to its users.
3. Finding the right partners and talent
Many businesses have trouble achieving their development objectives due to a lack of talent or support from partners. For example, an application used to organize and analyze patients’ records will need actual records to demonstrate that it works, which means cooperation with a hospital or clinic. Similarly, you may experience difficulty with hiring experienced specialists if you do not have them in your staff already. One solution in this case is finding a development partner with ready candidates (read more on that below).
Finding the Right Telemedicine App Developers
If you lack the time or resources to develop your application yourself, you can always hire a team to do it for you, or add to an existing team if you want to keep some of the development in-house. In these situations, a good development partner can be your saving grace, getting the project done according to your specifications. While there are many companies out there offering development services like the ones we described, not all of them have the reliability and experience to deliver high-quality results.

Program-Ace is an innovative company with 26 years of delivering digital solutions for different industries, including healthcare. Our main focus is on software development and design, though these skills extend in a range of directions, such as VR/AR/MR, digital twins, game design, 3D modeling, animation, and gamification. In healthcare, we developed the MoMedX solution previously mentioned, along with several other programs in the past and present.
With over 120 experienced specialists on our staff, we are more than ready to tackle projects of varying scope and difficulty. More importantly, we are ready to deliver high-quality results within the timeframes you provide. If you have any questions or want to discuss potential cooperation, you are welcome to contact us.
























