Each year, businesses look at the landscape of new technologies that become available and ask, “How can we use this to be more effective?” Terms like robotics, automation virtuality, and simulation get thrown around as potential solutions, and with good reason. Each brings something unique to business operations, but we want to focus on perhaps the most versatile solution – custom virtual reality training development.
Virtual reality (VR) is not just a tool for gaming. Businesses utilize more than half of the available headsets for non-commercial purposes. There is much to unpack here, and we will give you all the details about virtual reality training solutions.
Looking for a virtual reality training development company?
What Is Virtual Reality Training?
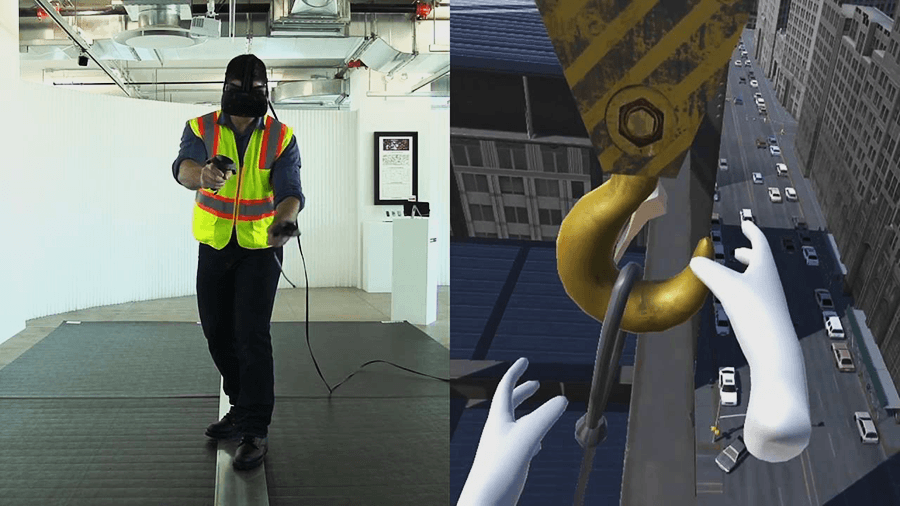

Virtual reality-based training (VRT) refers to training programs that are accessed with the help of virtual reality technology. Virtual reality (VR) devices usually consist of a headset/goggles and accessories like controllers, additional sensors, and gloves. These devices are connected to a computer/smartphone/another electronic gadget, and when the whole system is working properly, users can see and interact with simulated objects and environments in 3D.
However, a VR training tool requires more than a headset. The other key component is software – a VR application that holds all the content and interactions of the experience. Most companies using virtual reality training develop this software in-house or find a partner to deliver a custom-made application.
What are VR training benefits?
Wherever a VR training application is deployed, it can benefit those who learn via the application and those who provide the software/hardware. Below are some key advantages of using VR for training:
- Training in VR has no geographic or scheduling limitations. Virtual reality training simulations can be accessed virtually anywhere and at any time.
- VR training reduces cost. Traditional educational programs require the participation and engagement of experienced specialists working with beginners, while VR training does not.
- Virtual reality training eleminates safety risks. Some professions have a high level of danger, even during training phases. However, given the superb VR training effectiveness and safety profile, there is nearly no risk of real accidents.
- Training in VR gives freedom and flexibility. A virtual app's objects, environment, and scenarios can be modified with less effort than elements of a physical setting.
Comparative Analysis: VR Training vs. Traditional Educational Methods
We can compare virtual reality training and traditional educational methods with the immersive experience of a 3D movie and the classic engagement of a theater play. Both have unique allure and effectiveness, yet they cater to different senses, preferences, and learning environments.
Traditional Training Methods have stood the test of time, offering a tried-and-true approach to learning. The direct interaction between instructor and learner, the tangible materials, and the immediate feedback loop creates an environment conducive to a wide range of learning styles.
Old-school training fosters interpersonal skills, adaptability, and a personal touch in education. They allow instructors to adjust their teaching strategies dynamically in response to the learners' immediate needs. However, these methods can be resource-intensive, often requiring physical presence, which limits scalability and can incur significant costs regarding materials, space, and potential travel.
Virtual reality (VR) training, on the other hand, represents cutting edge of educational technology. It immerses learners in a fully controlled environment where every aspect of the experience can be designed to achieve specific learning outcomes. This immersive quality makes VR training particularly effective in scenarios too dangerous or impractical to replicate in real life, such as complex surgical procedures or handling hazardous materials.
Training in VR also offers unparalleled scalability and remote learning capabilities, transcending geographical barriers. However, the costs of developing and maintaining VR systems and the need for technical proficiency can be significant drawbacks. Additionally, the lack of personal interaction and potential technological limitations, such as the risk of VR-induced motion sickness, must be addressed.
Leveraging our experience developing VR training solutions, we distinguished scenarios where each method will blossom the best.
Choose VR Training:
- When training for high-risk tasks where safety is a concern.
- In scenarios where creating real-life situations is impractical or expensive.
- For technical training that benefits from visual and immersive experiences.
- When targeting a geographically dispersed audience.
Select Traditional Training:
- When interpersonal skills and direct human interaction are key learning outcomes.
- In environments with limited access to advanced technology.
- For subjects where adaptability and personalization by an instructor are crucial.
- When cost constraints limit the feasibility of high-tech solutions.
At the same time, companies can combine both approaches. The blend of virtual reality training and traditional methods creates a versatile learning environment where trainees can refine their skills in an all-around manner.
Technological Requirements for VR Training
Have you ever wondered what creating a truly immersive virtual reality (VR) training experience takes? The magic of VR training lies not just in the software but also in a symphony of hardware components and technologies working seamlessly together. Here's a closer look at the essential elements of VR training:
VR Headsets. The gateway to virtual reality, VR headsets range from high-end devices like the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive, offering rich graphics and detailed immersion, to more accessible options like the Oculus Quest, which trades some graphical fidelity for wireless convenience. The choice of headset impacts not only the visual quality but also the overall user experience in the VR training program.
Motion Tracking Technology. Essential for creating a realistic and interactive virtual reality (VR) environment, motion tracking technology varies in complexity. Systems like the HTC Vive use external sensors for precise tracking, while others, like the Oculus Rift S, employ inside-out tracking with built-in cameras. This technology ensures that the movements of VR training participants are accurately mirrored in the virtual world, enhancing the sense of immersion.
Computing Power. The backbone of training in VR, computing power, determines the smoothness and complexity of the experience. High-end virtual reality (VR) setups require powerful PCs with advanced graphics cards and processors to handle detailed simulations. In contrast, standalone VR headsets have built-in computing capabilities suitable for less graphically intensive applications.
Software Platforms. Choosing software platforms, such as Unity or Unreal Engine, is crucial for developing VR training content. These platforms offer a range of tools for creating immersive and interactive 3D environments. The software must be compatible with the chosen virtual reality (VR) hardware and flexible enough to accommodate updates and modifications to the VR training content.
Audio Equipment. Immersive audio enhances the realism of VR training, with options ranging from built-in headset audio to external noise-canceling headphones. High-quality, spatial audio is key to a fully immersive experience, helping users of VR training programs feel like they are truly part of the virtual environment.
Input Devices. Interactivity in VR training is facilitated by input devices like handheld controllers, haptic gloves, or even full-body tracking suits. These devices vary in complexity and functionality, offering different levels of interaction, from simple button presses to detailed hand gesture recognition, crucial for a realistic and engaging training experience.
Psychological Aspects of VR Training
Training in VR is not just a technological frontier, but also a rich field for psychological exploration. Its profound impact on learning and cognition reshapes how we understand and interact with educational content. At the heart of VR training's effectiveness is its ability to create a sense of presence, a feeling that one is truly 'inside' the virtual environment. This immersive quality fundamentally changes the learning experience.
When learners start their training in VR, they step into worlds where their cognitive processes are engaged in ways traditional classrooms seldom achieve. For instance, in VR training in the medical sector, students can perform surgical procedures in a hyper-realistic setting. This direct, experiential form of learning deepens their understanding and retention of complex medical procedures far more effectively than textbook study alone. The emotional connection forged in these VR training simulations, where a wrong decision could have 'life-threatening' consequences, even if only virtual, imprints lessons deeply in the learner's psyche.
However, the psychological impact of VR training extends beyond enhanced engagement. It also includes the potential for side effects like VR-induced motion sickness, a discomfort arising from the disconnect between what the eyes see and the body feels. This dissonance can be jarring, pulling learners out of the experience and sometimes causing physical discomfort. For instance, pilots training on VR training flight simulators might experience nausea as their visual field whirls while their bodies remain stationary.
Another consideration of VR training is the risk of desensitization, particularly in fields like military or emergency response training. Repeated exposure to high-stress, virtual scenarios could, over time, dull a trainee's emotional response to real-life emergencies. This desensitization could be a double-edged sword of training in VR, potentially beneficial in helping professionals maintain composure under pressure but also risky if it leads to underestimation of real-world dangers.
Moreover, the immersive nature of VR training can sometimes lead to cognitive overload, especially for novices. Being bombarded with stimuli in a 360-degree virtual environment can overwhelm the senses, making it hard to focus on the learning objectives. This sensory overload can be counterproductive, leading to confusion rather than clarity VR training promises.
But do not let these challenges discourage you from adopting virtual reality training. With readiness to deal with possible issues and strong technical backup, you can harness the full power of VR training within your company and set up effective and comprehensive interactive training courses.
VR Training Use Cases
Virtual reality training for employees
Using VR training in the workplace will surely cause a major shift in any business. Though companies must invest in the right hardware and software, many other costs and difficulties involved in employee education are removed or streamlined.
From a logistics viewpoint, companies don’t need to take employees to any special location to learn or provide them with working equipment. Instead, the workers are given everything they need in the VR training simulation, including a virtual reality trainer in some cases.
In terms of knowledge and skills, you can add the same information, text, and exercises in the VR training simulation as you could in a classroom setting and much more because 3D modeling allows you to create objects, settings, and scenarios that would not be feasible in real life.
Aircraft Engine Training in VR
Program-Ace developed this VR training application for HTC Vive and Oculus Rift devices. It is mainly targeted towards engineers and technicians who work with Rolls Royce jet engines and need to know their configuration intimately.
This application places employees in a room with a detailed 3D aircraft engine model. They can easily disassemble and assemble it with controllers, learning where each part goes and how it should be added/removed.
This form of corporate VR training gives employees the usual benefits of handling an engine without physical challenges and limitations.

Virtual reality training for clients/users
Many enterprises develop training applications with profit in mind, offering them to other businesses or consumers as a SaaS platform or paid app.
Apps geared towards educating everyday consumers are usually made available on the digital marketplaces of VR headset makers, where people who already own the hardware make the most of it by trying games and practical apps.
As for cases when the VR training app is meant for another business, the development is usually tailored to the business processes of that company and often just adapts an existing training program into a new digital medium.
Of course, some enterprises develop VR training software that can be used by numerous companies in a particular industry, even if they have different ways of doing things.
Hand Rehabilitation Training in VR
Our company developed this solution for a major medical provider in the U.S., but its universal functionality makes it a helpful tool for numerous hospitals and treatment programs.
This VR training experience is geared towards patients going through hand rehabilitation. If they have lost some movement capability, they can put on the VR headset and gloves and learn to restore movement with the help of a virtual trainer.
Their progress is recorded through exercises they try to complete with the gloves. At the same time, the digital assistant provides instructions and guidance, shifting the difficulty of the tasks up as patients improve.
Using VR for rehabilitation, this solution can easily replace visits to the doctor and lets patients heal at their own pace and in comfortable conditions.

Industry Examples of Virtual Reality Training
Virtual reality (VR) has permeated most industries already so we can find plenty of examples of enterprises in different fields using it for educational purposes. Let’s examine some of these notable uses of VR training:
VR training in sport
Helping athletes learn proper technique and grasp the physics of their chosen sport.
VR training in medicine
Medical practitioners can prepare for surgery, care, and even emergency procedures with a digital aid.
VR training in construction
Improving collaboration between construction workers and preparing them for operations in potentially-hazardous areas.
VR training in manufacturing
Manufacturing experts are using VR for test fixes and changes on the production line.
VR training in HR
Learning proper etiquette and helpful responses to difficult conversations with workers.
VR training in aviation
Using VR for flight simulators allows to upgrade them with many new features and interactions.
VR training in customer service
Management training in VR helps CS representatives develop crucial soft skills for customer service.
VR training in the military
Military personnel are using VR for numerous combat simulations to prepare for various situations on the battlefield.
VR training in law enforcement
Giving officers a better understanding of different crimes and how to apprehend criminals.
Demonstrating proper safety procedures to workers without putting them at risk.
And more
VR training can be found in practically every industry. You can find out more in our guide to immersive training.
How Much Does Virtual Reality Training Cost?
Most virtual reality training app development cycles add up to $50K-$1M in costs, depending on the project's scope. These figures are high mostly due to the labor cost – you will usually need multiple developers, 3D modelers, QA testers, and other experts working on the project for months before it reaches completion, and these professions are notoriously high-paying.
In addition, you will probably have to buy headsets for the people who test (and eventually use) your VR training application and licensing fees for software used during development. Most leading headsets cost between $400 and $700, though there are big differences in specs. For more information, check out our comparison of top VR headsets for development.
If virtual reality (VR) hardware and development costs are more than you care to invest, you can also consider the sister technology of VR – augmented reality. These apps require less coding and 3D assets and are much more accessible, running on most smartphones. If this option interests you, check out our augmented reality training landscape review.
How to Create VR Training for Your Enterprise
Have you made up your mind about creating your own immersive virtual reality training program? Using VR for employee education, intership or other activies opens a new dimension of opportunities, but first, you need consider the technical aspects.
The process can be an uphill climb for companies that accept this challenge for the first time. You need to gather the learning materials and scenarios that will be part of the VR training experience and some coding experience to develop your application on one of the major platforms (like Unity or Unreal Engine).
Naturally, you can hire a team of developers from virtual reality training companies to handle the process. You must evaluate their experience and portfolio and check the type of platforms they develop to ensure they are compatible with your needs.
Program-Ace is a company that knows how to make training in VR effective. We have over 26 years of experience developing custom VR training applications and other services like 3D modeling, game production, and design with VR/MR/AR.
If you reach out to us and share a few details about your virtual reality training, we will be pleased to give it a decisive push forward, even if it means we must create a virtual training environment from the ground up.


























