What is an industrial metaverse? The topic generated a lot of hype, especially after Facebook Inc. rebranded into Meta Platform Inc. to reflect the company's purpose in building the full-fledged metaverse. While the metaverse is strongly associated with social and entertainment in the collective consciousness, this breakthrough technology has much broader potential. It can drive value to enterprises in various industries.
Manufacturing is one sector that can benefit significantly from the metaverse. Mass implementation of such solutions has even distinguished a manufacturing-specific branch of this ecosystem called the industrial metaverse. So what capabilities do industrial metaverses have, and how do manufacturers leverage them? As a metaverse development company, we know the answers from firsthand experience.
What is the Industrial Metaverse?
The industrial metaverse definition implies implementing the metaverse for the manufacturing, construction, and engineering sectors, which creates an online, highly immersive virtual environment for specialists to collaborate remotely or build simulations.
One of the primary building blocks of the industrial metaverse ecosystem is digital twins. This technology allows the creation of identical online copies of particular physical objects, systems, or processes. However, a digital twin is more than a simple duplicate. The difference is that a digital twin is linked to its physical counterpart and receives real-time updates. The convergence and visibility of the metaverse and digital twins facilitate the precise integration of real-life entities like equipment and machinery into the virtual dimension, ensuring that any manipulation will correspond with how things are in reality.
Why is the industrial metaverse important?
The industrial metaverse presents a spectrum of technological possibilities that promise significant opportunities in the future. PTC envisions revolutionizing collaboration within the industrial sector, enhancing factory productivity, and optimizing design procedures. Take, for instance, a scenario where a complex piece of machinery malfunctions in a remote location. While video calls with remote experts assist, they often need physical inspection to diagnose the issue accurately.
Traditionally, sending an expert onsite would be the only recourse, a costly and time-consuming endeavor that exacerbates equipment downtime. However, remote experts can swiftly gain a comprehensive, contextualized view of the problem with the industrial metaverse within minutes. Leveraging spatial technology, PTC's innovative approach allows individuals to access an online environment via smartphones, enabling them to troubleshoot and collaborate with onsite personnel effectively. This solution facilitates seamless communication, network, and problem-solving between onsite workers and experts by providing data in a spatial context.
Another scenario illustrates the practical applications of industrial metaverse technology: a technician suspects machinery is yielding subpar products. Using their smartphone camera to scan the equipment and its surroundings, the technician generates a link to a "pop-up" metaverse, which can be shared with a remote expert. Through PTC's technology, the expert can seamlessly join the virtual and online space, maneuvering around as if physically present and scrutinizing the environment through their device.
This immersive experience allows them to zoom in on specific items for visual inspection and access pertinent digital information within context, such as repair history and performance data. These examples of the industrial metaverse are not merely futuristic concepts; PTC has been actively developing and refining this technology for years, positioning itself as leader in the industry. With PTC's existing technology, companies can address spatial challenges with unparalleled efficiency and precision.
Beyond instantaneous spatial collaboration, remote experts can utilize data gathered from workers, products, and machinery movement within a space, such as a factory floor. Leveraging spatial analytics, they can identify opportunities to enhance performance, streamline operations, and annotate a digital ledger within the space.
Moreover, by maintaining a volumetric scan of the space over time, remote experts can detect anomalies and deviations from previous configurations, providing insights into changes on the shop floor or field where equipment is deployed. Embracing emerging technologies like the industrial metaverse enables companies to stay ahead of the curve, facilitating quicker adaptation and the expansion of use cases as advancements continue to evolve.
The Evolution of the Industrial Metaverse
Modern manufacturing and related sectors are experiencing the Fourth Industrial Revolution, a rapid leveling up of the processes, approaches, and mechanics brought by the development of profound innovations, namely smart automation. The key technologies that drive change include the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, machine learning, advanced robotics, 3D modeling, and others.
So what about the metaverse? Is humanity going through the metaverse industrial revolution right now? While the metaverse trends are gaining popularity, we must catch up to its mass implementation. The high-level concept of the metaverse implies the existence of a fully-fledged online dimension that users can easily explore through virtual avatars. This requires advanced interconnectivity, robust and scalable infrastructure, and the widespread adoption of VR/AR/MR devices, and we still need to reach such a state.
As for now, the metaverse looks like a set of separate virtual dimensions instead of an interconnected virtual world. In the industrial environment, most enterprises only start to explore the full capabilities of the metaverse, transferring merely some processes there. However, some market leaders adopt industrial metaverse solutions faster. They show that it’s possible to create full-scale factories in the virtual dimension and remove physical barriers and limitations, creating a vision for the future path of industrial metaverse development.
Industrial Metaverse Market Size
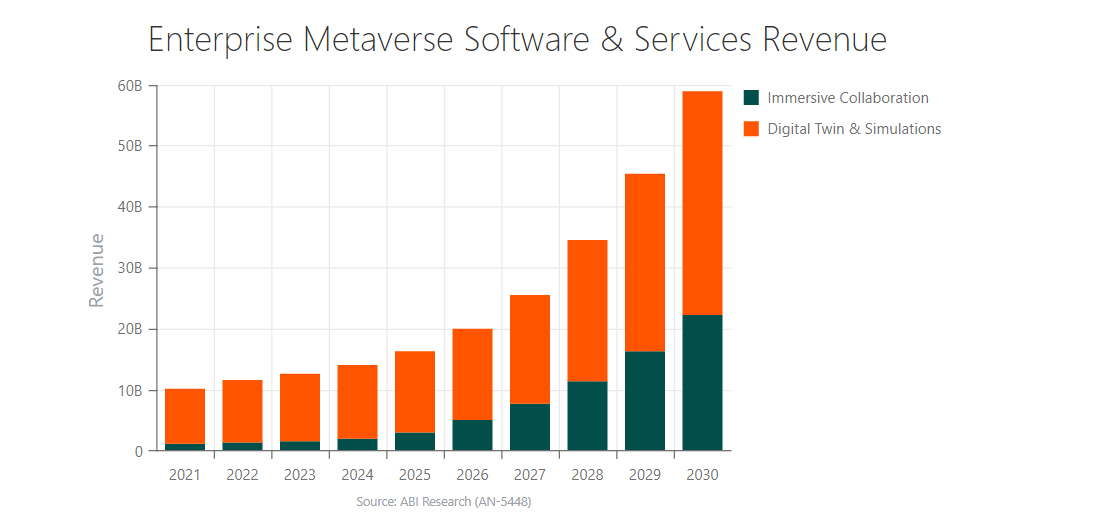
The industrial metaverse market is built on immersive collaboration and digital twins/simulations, and according to researchers, the revenues from these aspects are predicted to reach $58.9 bn by 2030. At the same time, the enterprise metaverse market is splintered, as most companies that offer metaverse-based solutions set up their standards and regulations for the network. Therefore, there is a problem of lack of interoperability, creating a challenge for further market growth. The answer would be standardization, which industry players will initiate and adopt.
The True Value of Industrial Metaverse
Even in the relatively early stages of its formation, the industrial metaverse can drive change and reinvent most processes. Implementing the industrial metaverse allows the optimization workflow and the transition from reactive to preventive or predictive approaches.
The metaverse empowers precise simulations, making it possible to manipulate virtual counterparts of real-world entities without dealing with physical limits or risking jeopardizing system performance. Thanks to this, it’s possible to enhance production speed, ensure a higher quality and lower amount of defective products, optimize expenses, prolong equipment life, increase safety, and relieve employees from mundane, repetitive tasks. Overall, the metaverse paves the road for the rise of virtual factories that will transform manufacturing beyond recognition.

Industrial Metaverse Use Cases

The metaverse use cases in the industrial sector vary and cover a lot of processes that occur on-site. Market leaders push sector innovations forward as they show readiness to dedicate their investments to technological updates in their factories, equipment, hardware, or software. Here are a few examples of how manufacturers leverage metaverse and related technologies to improve workflow.
1. Employee Training in the Metaverse
Using the metaverse expands training and education capabilities, making it more accessible, safe, and efficient than the traditional approach. Therefore, companies have increasingly decided to leverage VR and simulation to teach their employees the necessary skills, submerge them into real-life conditions without jeopardizing their safety, and remove physical barriers that might create obstacles to smooth collaboration and learning.
First, manufacturers can create identical virtual copies of equipment or heavy machinery to introduce new employees in a controlled, accident-free environment. It also increases the quality of the training, as trainees get a chance to study a piece of equipment in and out, which might be impossible in real life.
Second, metaverse training empowers immersive hazardous scenarios training. Safety instructors can simulate dangerous situations instead of conducting a simple briefing and going through the cause of actions with employees. This way, employees can acquire fundamental skills to act in hazardous conditions and remember them during an accident.
Third, the metaverse allows the creating a 3D model virtual database of equipment or other items. They can be available for any employee at any time of the day, so specialists can deepen their knowledge and skills whenever needed without disrupting the production process or requiring the assistance of other team members.
2. Virtual Collaboration in the Metaverse for Designing or Maintenance
The precise simulation reinvents traditional approaches to product design and facility maintenance. Through the metaverse capacities, specialists don't need to figure out the issues or resolve challenges on the go when operating with physical entities. Real-life objects can be easily replaced with digital copies, and manipulating any virtual object is much easier than a real one.
In terms of product design, implementing the metaverse means giving out physical prototyping and moving to the virtual dimension, which demands fewer resources and where your testing capacities are much broader. Maintenance also becomes more efficient because manufacturers can monitor the state of equipment in real time and predict breakages before they happen, therefore applying preventive measures.
Another significant benefit is remote collaboration. The metaverse exists in the virtual dimension, and users can access it anywhere. Hence, remote specialists or invited experts don't need to travel miles to visit your factory or plant on-site; they can put on a VR set and find themselves in a virtual copy of your facility. And with high simulation accuracy, experts accessing you through the metaverse will be able to perform at the same level as they would if visiting in real life.
3. Metaverse-powered Virtual Simulation for Optimization
Digital twins, a core technology for the industrial metaverse we have already mentioned, enable advanced optimization for manufacturers. A digital twin goes beyond simulating a single object: a business can build a set of duplicates and simulate a production floor, a whole department, or even a whole factory. While testing different scenarios with their help, businesses can detect bottlenecks, systems' weak spots, and other issues that slow down growth or waste resources, taking appropriate measures in real life to remove any obstacles.
At the same time, specialists can use digital twins to trial-test their improvement hypothesis to see how it will impact the entire system. This evaluation will help them understand the practicality of suggested optimization and avoid dedicating investments, time, and human efforts to an idea doomed to fail from the start.

4. Introduction of Virtual Designs Created in the Metaverse
Besides incorporating changes into internal processes, the metaverse can transform business and customer relationships. As the physical and virtual borders become thinner, manufacturers can use this to create new revenue streams.
Virtual designs are one way this concept might work. When entering the metaverse, clients can create their designs of the brand's product or application, whether a pair of shoes, a furniture set, or even something more substantial, like a detail for a particular vehicle. Then, a manufacturer will build this product and ship it to the customer, who will receive a product customized by their own hands.
Tap into the Industrial Metaverse with the Help of Program-Ace
The industrial metaverse promises a lot to manufacturers who dare to explore such innovative technologies. This technology has already started to revolutionize manufacturing, putting the metaverse enthusiast in the lead, and the future looks even brighter for those businesses that are not afraid to break the barriers between physical and virtual.
However, implementing the metaverse isn't a cakewalk. To achieve actual results, you need a solid technical team that will help you approach the metaverse correctly. Program-Ace, a custom software development company with significant experience with metaverse solutions, can guide you through the possible challenges and reveal the full potential of the industrial metaverse. Feel free to contact us to discuss the details and initiate cooperation.






















