Every year in dozens of locations around the world, numerous expos and conferences are held, showcasing tech companies’ greatest achievements of the past year. These events bring a flurry of exciting new inventions that lend themselves to buzz-worthy news headlines, but many other innovations remain below the radar and out of the public eye. WebAR as an offshoot of AR development services is indubitably one of these low-key breakthroughs of recent years. Most modern consumers have probably never heard of it, yet the technology will make its way into their lives sooner rather than later.
If properly utilized, WebAR can work wonders for businesses, adding value to their products and services while upending major business strategies. Program-Ace is an augmented reality application development company with over 10 years of experience - ready to provide you with all the essential details.
Looking for AR developers?
What is WebAR?

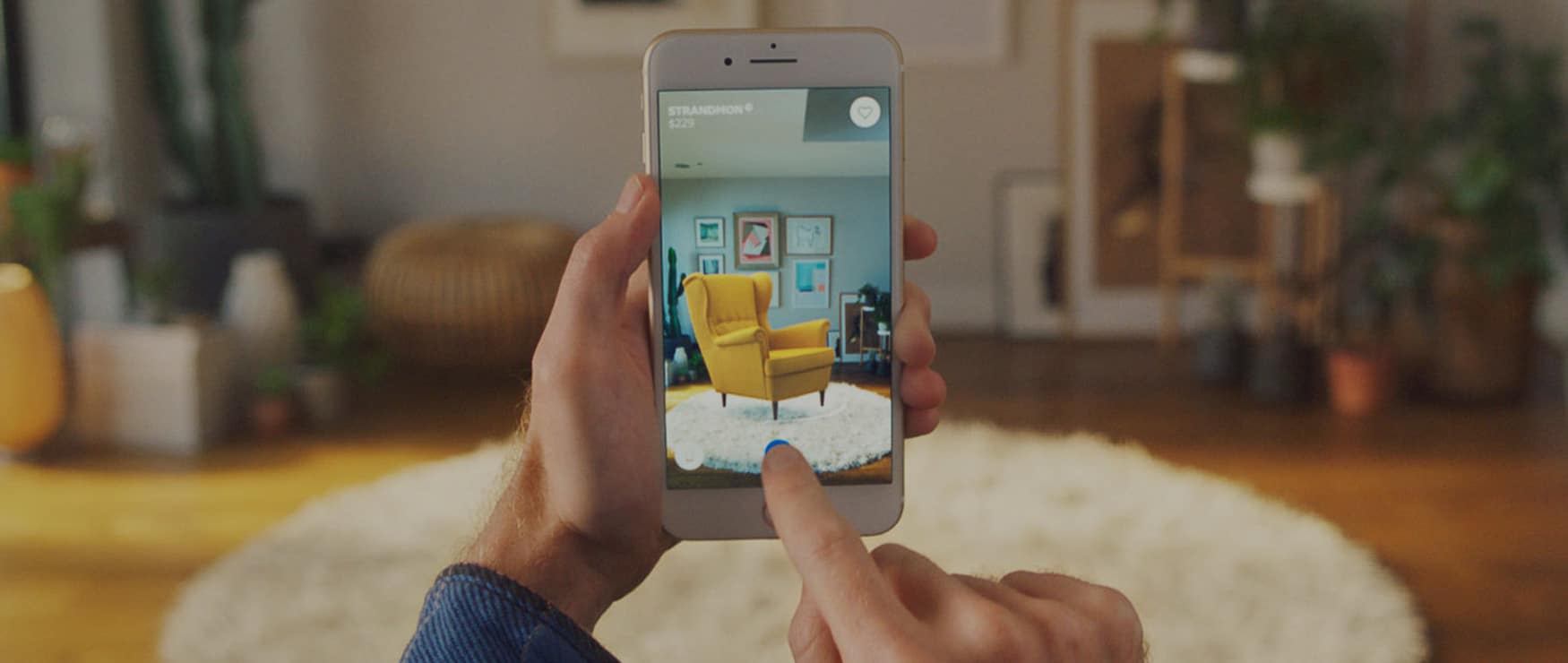
WebAR refers to web-based augmented reality, which overlays digital elements in a real-life setting captured on camera. The overlay and its end result are displayed in a web browser. For the technology to work, a user must be operating a digital device with a screen and a camera. Usually, this is a mobile phone or tablet, since other devices like laptops, music players, and consoles typically lack the mobility or functionality required to fully convey augmented reality experiences.
How does WebAR work
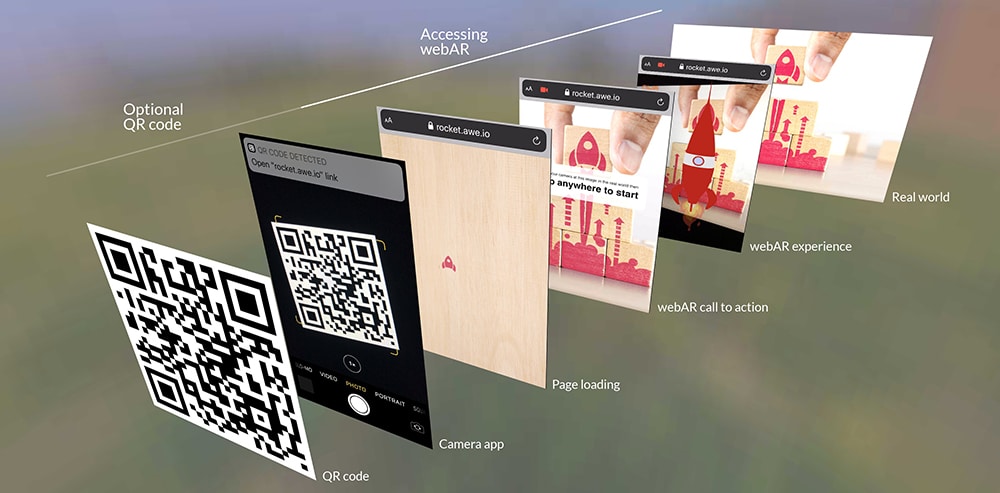
- Any WebAR experience begins with a user visiting a webpage in their device’s browser. This webpage will contain the application that will deliver the augmented experience and will begin loading most of the data needed to enjoy the session. Usually, at this point, the browser will ask the phone/tablet for permission to access the device’s camera (and possibly other tools), which is essential for what comes next.
- With all permissions granted, the browser window shows the visuals being captured live by the camera and analyzes the setting for further augmentation. The app may look for pre-determined objects (markers) in the visuals and add digital elements based on where these markers are, or use a markerless approach, analyzing the visuals’ lighting, distance, depth, and other characteristics to determine where to display the digital models.
- And, Voila! The user is treated to a unique set of visuals directly in their browser window, which feature a mix of real and virtual elements. It could be a 3D chair hovering in the air, an animated character talking to them, or anything else that the app developers can think to visualize.
WebAR Compared to Standalone Apps
The reason why so much buzz is being created about WebAR is because it reimagines what an augmented reality application must be. In the decades since the first AR apps appeared, nearly all of them were standalone apps downloaded from an app store to a mobile device. When WebAR came along, it pushed the bar on what users could do in their web browser and proved that businesses could provide AR experiences analogous to standalone apps without the hassle of getting their app approved by app stores and asking their users to clutter up their phones’ memory with an unnecessary download.
Where WebAR Can Be Used
Considering that the technology has already been around for several years, we do not need to make predictions about the industries it can be used, and can instead rely on real-world data and examples.
Interior design

Many people look for home accessories online and do it on their smartphones. Thus, it only makes sense for stores to add AR capability to their website, allowing users to see how the item will look in their home. The same approach can be used for designers and planners as they visualize the kind of changes they want to make in the home. Furthermore, real estate agents can provide such a tool to customers to give them an idea of how their belongings will look in an otherwise empty house.
For example, Samsung recently debuted a solution featuring products from their upcoming Virtual Home release. To get the experience, people only needed to scan a QR code and the home objects would appear on their screen.
Entertainment

One thing many people forget about augmented reality is that it is not limited to static objects and models: moving objects, animations, and sound can also be added, making the experience more exciting. This is especially useful in the entertainment industry, where everything is centered around performers and artists, as well as the media they produce.
For example, Burger King recently partnered with a rapper called Tinie Tempah to promote his music and their Whopper burger. Users would scan a code on their Whopper packaging and the rapper would appear, dancing on top of the burger and performing his latest single.
Brand marketing

Given the novelty of the WebAR experience, it should not be surprising that brands and marketing agencies would want to capitalize on this kind of solution. After all, if they give the consumer something that engages them and which they haven’t seen before, the person will be much more likely to keep interacting with the brand. This is an approach that Coca Cola tested in South Africa, giving customers the amusing opportunity to view themselves and their friends with filters featuring bottles and caps.
Education

Apart from promotion and customization, there is intrinsic educational value in WebAR platforms, as they can visualize important topics and concepts in a much more relatable way than a textbook or even a video presentation. We have seen this proven with Below the Surface, an online experience that visualizes the devastating effects and waste caused by the global fishing industry.
Automobile

Automakers are no stranger to using innovative and immersive tech solutions, from configurators to driving simulators and virtual tours. Thus, using WebAR is the next logical step for them, and we are already seeing it happen. Volvo has produced a unique experience for their customers that shows off their new S60 model directly in their phones. They can see it in different variations, colors, and even schedule a test drive.
Other
Some of the technology’s uses are not limited to a particular market or niche, and are rather a general asset that can help most businesses. For example, it can be used in corporate training. Porsche delivered a unique training program for employees that can be enjoyed in any location. They just need to open the online app and see the company history, values, and other essential information visualized before their eyes. Other industries where WebAR has already been used effectively:
- Manufacturing
- Gaming
- Construction
- Energy
- Healthcare
Potential Drawbacks of WebAR
With all of the benefits demonstrated in our examples, you might think that this type of platform is the gold standard in immersion, but this is hardly the case. There are some potential drawbacks when you opt for this kind of platform:
Internet requirements
Some of the applications developed in this field are very resource-heavy, and require the browser to download lots of data to deliver the full experience. For users with a slow connection or a limited amount of available bandwidth, this could be an inconvenience. For example, the Waterloo train station in London featured AR-enabled posters which can be scanned from a website to display live train arrival/departure times. The experience was made possible through connections to the website API, so a constant stream of data was required to get up-to-date information.
Limits of the browser
We have mentioned that web apps of this kind require certain permissions from the phone, so they are limited in regards to what the phone allows the web browser to do. Accordingly, phone features like Bluetooth, NFC, and facial recognition may not be accessible to the browser as they are accessible to standalone apps. For example, a beer company called Multi-Color Corporation created a standalone mobile app with an experience difficult to replicate on a website: after a user scans an NFC label on a beer bottle, they see a talking skull appear in the app that will interact with them based on their facial expressions captured by the device.
Supported browsers
Unfortunately, millions of users with smartphones may not be able to access AR apps online due to their browser. Not all browsers are built alike, and many fail to add support for XR technologies even in their updates. Default (pre-installed) browsers from phone-makers are the biggest culprit, but another major browser affected is Opera Mini, which has more than 200 million active users.
Supported hardware
It also sometimes happens that the platform is not supported by the hardware – the phone or gadget used to access the site. Most of the time, it is due to a lack of camera on the device, but it can also be a device so old that it barely opens webpages and fails to run even the simplest scripts.
The Future of WebAR
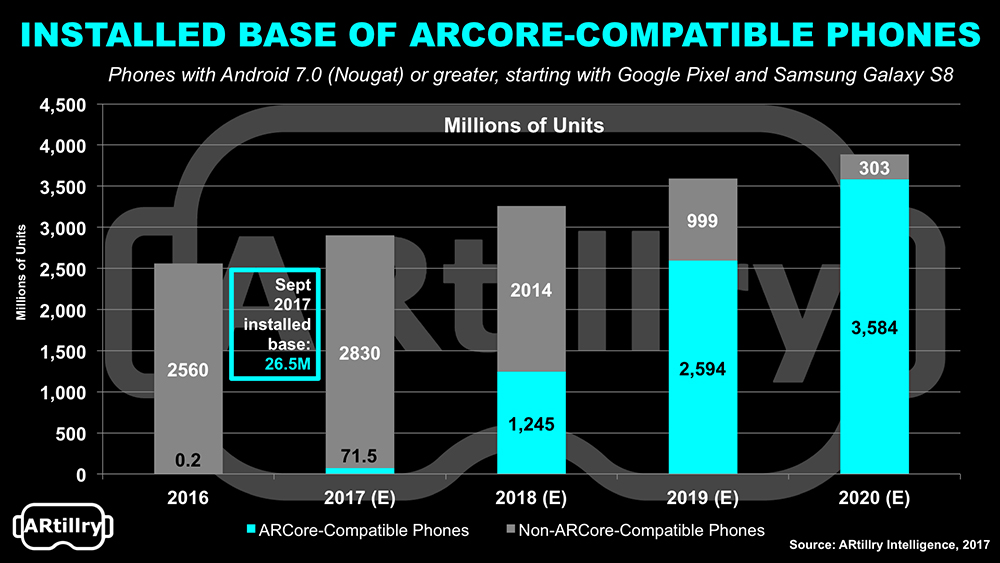
We can do our best at predicting the future by looking at the past and present. Though the technology is quite new, there are already multiple positive indicators. A projected 92% of Android phones (3.6 billion units) already support WebAR, and it would be a safe bet to say that the percentage for iOS devices is similar. Furthermore, about 97% of the world’s biggest brands already use augmented reality solutions, with smaller businesses gradually following in their footsteps.
All of this amounts to a fertile breeding ground for innovation. As the popularity of WebAR experiences grows, we can expect them to become more elaborate, providing users with increased functionality and possibly taking up dozens of pages on a website. Still, it is important to remember that people prefer to get their information and entertainment from different forms of media, so we are unlikely to see this platform replace all others that currently dominate the field.
Most likely, it will serve as a valuable addition to company websites and standalone apps for users who want to learn about a brand and receive some level of immersion without downloading a bulky mobile app.
How WebAR Development Takes Place
Projects of this type are typically handled by web development teams with a good background in mobile and AR solutions. For example, a project aiming to visualize a single and simple product will usually require a project manager, 1-2 developers, a 3D artist, and a QA engineer. Accordingly, more elaborate experiences will require more specialists and more time.
As is the case with most other software-based visualization projects, the key tasks that go into the project will include writing the code for the functionality, creating 3D models with required effects and animation, establishing networking settings, scaling for multiple browsers and devices, configuring the backend for numerous simultaneous connections, and testing everything. Development will typically last anywhere between several weeks and a year.
How Can I Set Up a WebAR App for My Business?
For specialists unfamiliar with the platform, mastering the learning curve can take weeks or months. Thus, the easiest solution available to businesses that want to integrate such a web solution is to hire a partner that will handle its development. For example, you can consider Program-Ace.
Our company has years of experience with AR, and we have achieved mastery in building solutions like product configurators, UIs, gamified apps, and countless others. Mobile and web applications are a given, but we also support other projects of extended reality (MR, VR), custom software development, game-making, and 3D art services. You are welcome to check out our portfolio.
Every great collaboration starts with a conversation, and we would love to get the ball rolling with you. To discuss your project and possible cooperation, just shoot us a message.



























