The manufacturing sector is no stranger to fierce competition, particularly when there are several alternatives for any given product from different competitors. In such a landscape, staying ahead requires innovation, efficiency, and adaptability. Many companies have realized this and embraced digital transformation as a way to remain competitive, introducing advanced solutions into their manufacturing processes. This strategic move has led to significant improvements, enhancing operational efficiency, product quality, and ultimately driving notable gains in profitability.
Digital transformation encompasses a range of approaches, and recent years have seen methods like gamification, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), and immersive experiences rapidly gaining traction. These approaches help streamline processes, engage employees, and improve product development, making now the perfect time to dive deeper into augmented reality app development services. Augmented reality (AR) has emerged as one of the most powerful and versatile tools within digital transformation — a technology that offers practical solutions for visualization, training, and real-time collaboration.
Leveraging augmented reality app development services, manufacturers can bring unprecedented levels of efficiency and innovation to their operations. In this article, we will explore the most effective applications of AR in manufacturing, providing insights into how this technology can be leveraged to maximize value while weighing its advantages and potential challenges.
What are the Benefits of Augmented Reality in Manufacturing?
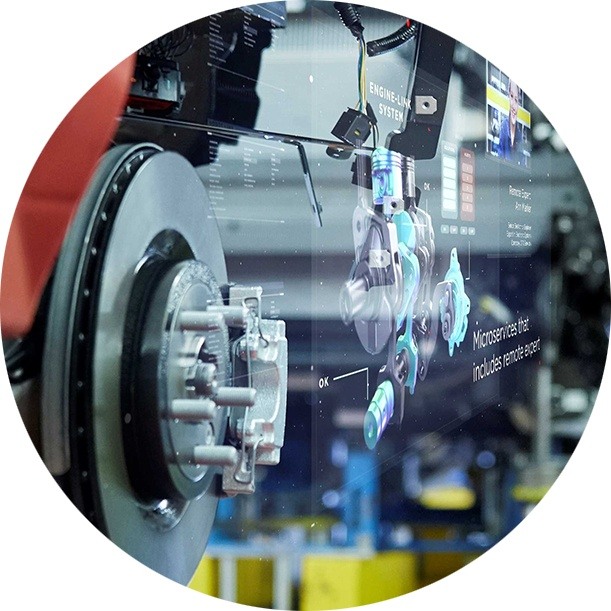

Augmented reality technology uses a device's camera to capture live footage and display it on a screen with overlaid 3D elements, creating an interactive experience. Users can see enhanced versions of their real environment by combining digital and physical components. Unlike virtual reality (VR), augmented reality does not require specialized headsets that cover the entire field of view or specific controllers to simulate motion. AR provides a practical approach by visualizing selected elements in the real world.
When comparing virtual and augmented reality for digital transformation in manufacturing, AR stands out as the most accessible immersive technology. It works seamlessly on a wide range of Android and iOS devices equipped with a functional camera, making it a practical solution for manufacturers without the need for expensive, specialized hardware. In contrast, VR demands significant investment in dedicated headsets and other equipment, which can be a barrier for many companies.
Moreover, AR has become a valuable tool in Product Lifecycle Management (PLM), supporting various stages of a product’s development, from concept visualization to design validation and customer engagement. This simplicity in deployment makes AR an attractive option for manufacturing companies looking to boost productivity and collaboration without major infrastructure investments. Additionally, AR enables remote assistance, interactive training, and real-time problem-solving capabilities, essential for efficient manufacturing operations. Other benefits of AR include:
Remote productivity
By creating digital constructs directly on the user’s screen, AR makes it possible to do work and other tasks in virtually any location.
Instant object recognition
Through advanced tracking software, AR apps can scan objects and settings and pick up details and conclusions that would be difficult or impossible for ordinary workers to reach.
Lifelike simulations at scale
Most AR apps have sufficiently elaborate coding that allows them to properly recognize surfaces and measure distance & scale. As a result, the digital elements they visualize are lifelike in scale.
Increased worker engagement
Immersive apps are exciting to use mostly due to their novelty and the sleek 3D models that provide a unique experience not found in everyday life. These factors work well to boost engagement.
Reduced cost and risk
In many cases, AR apps can replace the work or function of real equipment or people. This helps save costs and keeps workers out of risky situations or hazardous conditions.
You can find more tangible and industry-specific examples of AR benefits in the next section.
6 Types of Manufacturing Apps You Can Build with AR
AR as an open technology has existed for at least a decade, and this time has allowed manufacturing companies all around the world to come up with all kinds of cool and creative applications for it. Let’s examine some of the most common choices and the peculiarities of their development.
1. Virtual training
About
Training apps are among the most common examples discussed here. Augmented reality in manufacturing training offers significant convenience for employee education, as it allows access from anywhere and can fully or partially replace human trainers. Moreover, it requires no specialized equipment or machinery, as everything can be visualized in 3D.
Development
Creating a training app requires lots of adaptation. First, you have plenty of learning materials and instructions that must be fit and organized on a small screen. Secondly, you have the objects that the interactions will focus on — often complex machines or equipment involved in production. These objects can be “adapted” with the help of scans and photogrammetry or custom modeling based on blueprints/schematics.
Example
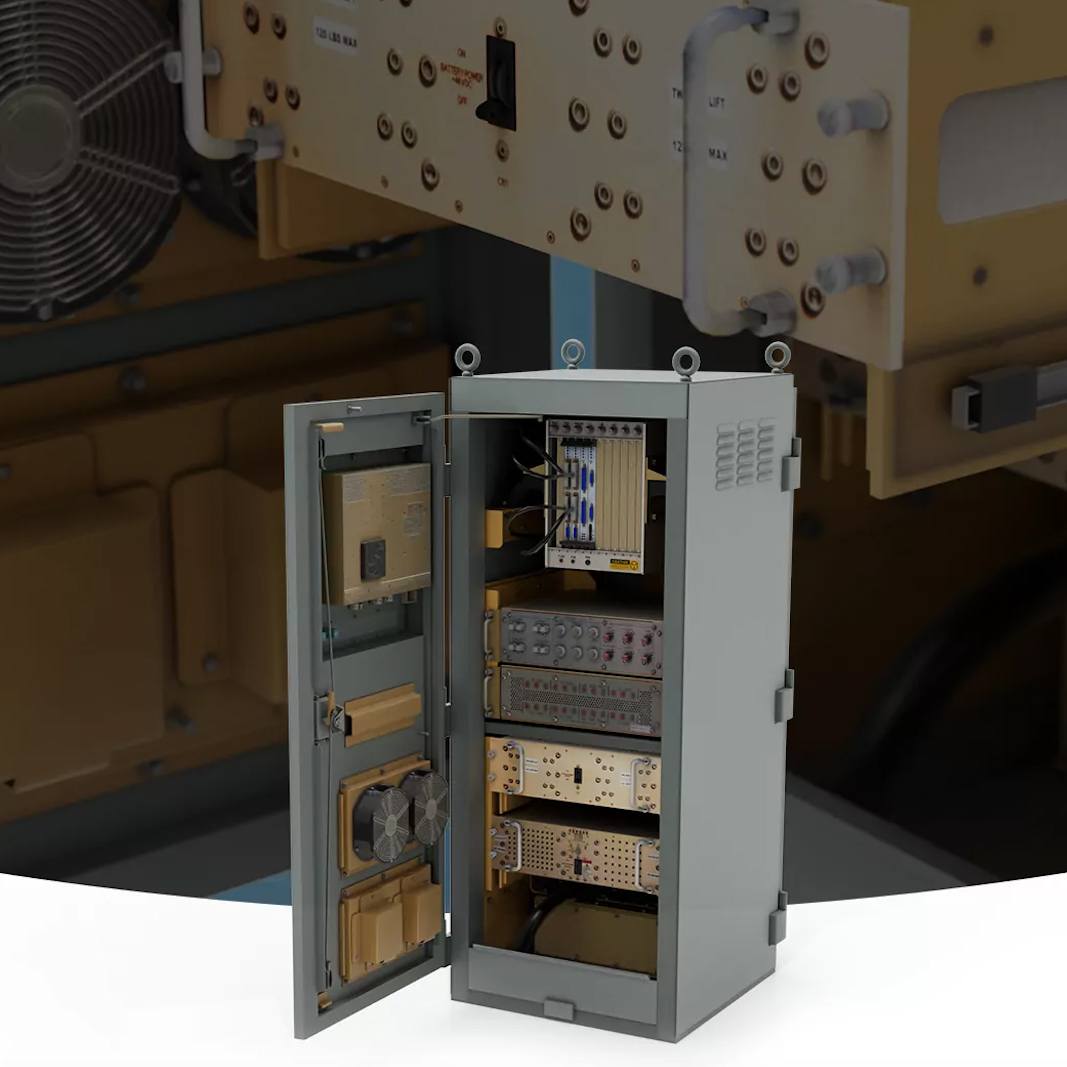

The Engine Control Unit is a complex piece of machinery used in ships and marine vessels. Program-Ace developed an application with multiple use purposes. In terms of manufacturing, it helps workers understand the internal and external structure of the unit and learn how the various parts deliver functionality. With this knowledge (and helpful animations and instructions), they can learn the proper order of assembly.
2. Collaboration apps

About
Most collaboration applications that make use of augmented reality are focused on remote troubleshooting. Thus, one user may open the app and focus the camera on a certain troublesome process/object, while another user with the same app open will see the feed and communicate with the first about resolving the issue. The AR elements may simply be a marker-based scanning system that identifies issues or a visualization that pops up with information about the issue.
Development
Networking features are a must-have in these types of apps, so you should make sure that your back-end is prepared to handle the flow of connections and potentially video streaming capabilities. Furthermore, the recognition features built into the app may be based on markers (pre-programmed visuals that the app looks for and activates when found) or be markerless (recognize objects and their states based on visual analysis and machine learning).
Example
PTC's Vuforia Chalk is a prime example of AR-based collaboration for remote troubleshooting. This application allows users to share live video feeds of equipment or processes while others can view the same feed and offer real-time guidance. By integrating visual annotations directly into the live scene, the app enhances understanding and accelerates problem-solving, making it highly effective for remote technical support in manufacturing environments.
3. Digital Twin

About
A digital twin is a digital representation of an object, system, or process. In manufacturing, this twin might replicate anything as small as a tiny component and as large as an entire supply chain. As a rule, the software of the twin analyzes how the object/system/process is working based on real measurements, while the AR features provide stunning visuals and relevant data that the user can understand.
Development
Digital twin development is a bit trickier than it is for other software types because the interactive models that will be presented through AR must perform exactly as the object does in real life. Thus, sensors and measurements are applied to the object and the data collected from a certain period of functioning must be converted into digital form. In other aspects, the process of creating the model and making it immersive is pretty standard.
Example
Siemens has leveraged digital twin technology in its Amberg electronics factory to optimize production and maintenance processes. The digital twin replicates the entire production system, using real-time data from sensors to monitor and analyze equipment performance. Such an approach allows workers to identify potential issues early, perform predictive maintenance, and improve overall efficiency. Combining digital twins and AR visualization helps employees interact with complex data intuitively, leading to enhanced decision-making and operational improvements.
4. Product or process configurators

About
An AR product configurator is a solution meant to bridge the gap between product design and sale. It typically provides a user with one product and dozens of customization options for it. The user tinkers with the configurator until they find the build they like most, and can then place an order for the item. This type of solution is helpful to production companies since they can present the full scale and variety of a product they produce in an organized and appealing way.
Development
Configurators can be made as simple or complex as you need them. For example, you might give the user a few menus of options and static 3D models that go along with them or choose a more dedicated approach, featuring updates in real time, responsive feedback, location-based suggestions, and even gesture tracking.
Example
FurnitARe is an application developed by Program-Ace and made free to use for furniture makers and consumers alike. For manufacturers, it is a great platform to add their inventory in all of its splendor. In turn, users can check how the furniture will look in their home, office, or another setting.
5. Visualization apps

About
Visualization can serve both as a part of broader functionality or a standalone solution. As a standalone solution, it essentially gives viewers a 3D representation of an object or setting, possibly with the addition of interactive options, special effects, and animation. In an industrial setting, it is great for presentations – demonstrating how something will look or work before primary work begins or the item is enabled.
Development
During development, you will first need to establish what will be visualized (data, a product, functions and processes, etc.). With this objective in mind, you can use relevant 3D software and AR SDKs to build and customize the software according to your needs, or those of your customers.
Example
General Electric (GE) has developed an AR app to help customers visualize various industrial equipment, such as turbines and generators, in 3D. This allows potential buyers to see the scale, design, and operational details of the equipment within their own facilities. By offering an immersive experience, GE enhances customer understanding and engagement, ultimately facilitating more informed purchasing decisions.
6. Prototyping software

About
AR apps can be a great boost when designing a new product or unit. As you come up with new designs and functionality, you can use the app as a sort of simulation center. It can help you see how the unit will function, calculate potential issues and defects, and even serve as a sandbox where you craft the model.
Development
Prototyping software comes in many varieties, but a uniting feature in most of them seems to be elaborate interactions with a 3D model. You may also need to create animations for the model(s) in motion and add customization options that affect how the model looks/performs. This is if the design process takes place in-app.
Example
Ford has integrated augmented reality into their prototyping process using AR applications to visualize vehicle designs and test component placements. Engineers can view virtual prototypes through AR devices, enabling them to assess the fit and function of components before physical production. This approach reduces the need for multiple physical prototypes, saving time and resources and helps address design challenges earlier in the development process.
And don’t forget - #7 – Custom! The sky is the limit for your creativity, so if you have an idea that falls outside these categories, you are welcome to develop it and become a pioneer of sorts.
Challenges You May Face During Development
Besides the obvious challenges connected with creating any mobile app, AR adds an additional level of difficulty to the development process, especially when the software is tailored to an industry as demanding as manufacturing. Below are some of the issues and challenges you may face if you set out on this path:
Making use of connectivity and storage
Delivering optimal content delivery through AR apps can be a challenge due to network and storage constraints. For example, if the app performs numerous downloads of interactive 3D models, each one can take a long time and might not be feasible in every location and internet connection. On the other hand, adding too much high-resolution content can make your app size balloon, creating a hassle for users with limited storage space. Most of the time, these issues can be overcome, but you have to find the right balance of network-accessed and pre-loaded features.
Large volume of required 3D assets
Accurate and lifelike simulations are formed with a variety of 3D models, all ranging in their size and level of detail. Those unfamiliar with the modeling process sometimes assume that they can get the 3D content in a matter of days, but it ends up taking weeks or months. If you are looking to recreate work settings and equipment with a high level of detail, be prepared to devote lots of time to modeling, even if you have more than one artist working on the task.
Creation of reliable markers
It’s not overwhelmingly difficult to create markers for the objects your app must recognize, but it is a lot harder to make the recognition system work under unique user conditions. For example, factors such as lighting, picture quality, and angle can all make it harder for recognition to occur. Furthermore, if the object is fully or partially blocked by something in the user’s surroundings, it may be impossible to complete recognition without removing the obstruction.
Productivity impeded by handheld devices
For most AR devices (phones), you can only make the most of the features by holding them in your hands and making some movements on the screen. While this is fine for learning simulations, it becomes a problem when you are doing a task that requires both hands. Obviously, you cannot competently operate a machine while holding your phone up and interacting with it, so the interactions must be designed in a way that does not distract from work.
Inconvenient interactions with complex models
Most manufacturing machinery is large and complex (at least on the inside), so it is best viewed on a large screen. While smartphones have been getting bigger over the past decade, they can sometimes be unwieldy when looking at large and complicated 3D models, such as those that are involved in augmented reality in pharma manufacturing. This challenge can be partly mitigated by adding zoom features to the model, but users may still not be able to make out the fine details of your objects when looking at them whilst zoomed out.
Choosing the Right Augmented Reality Manufacturing Companies
For one reason or another, independent development may not be in the cards for every business. Oftentimes, this is simply due to a lack of experience and suitable specialists. Whatever it is that is holding your company back from development, you can probably mitigate it by finding a development partner that will take care of the process for you.
Program-Ace is a custom software development company that operates in the fields of immersive apps. We have crafted dozens of effective solutions in the manufacturing industry, including the Engine Control Unit previously mentioned. Decades of work in addressing enterprises’ needs have taught us how to build software that will bring substantial use and value to the company, and which won’t soon be forgotten.
In case you want to know more about our services or ask about potential cooperation, feel free to contact us.























